The key difference between somatogenic and blastogenic variation is that somatogenic variation affects somatic body cells of an organism and is not inheritable, while blastogeic variation affects germ cells of an organism and is inheritable.
Variation is the morphological, physiological, cytological, or behaviouristic differences among individuals of the same species and offspring of the same parents. They can be found in all characters. Therefore, no two individuals are similar due to these variations. Variations even take place in clones and monozygotic twins. Variation is classified based on different factors such as affected trait, impact, parts, degree, cells affected (somatogenic and blastogenic), etc. Somatogenic and blastogenic variations are two types of variations according to the cells affected in an organism.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Somatogenic Variation
3. What is Blastogenic Variation
4. Similarities – Somatogenic and Blastogenic Variation
5. Somatogenic vs Blastogenic Variation in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Somatogenic vs Blastogenic Variation
What is Somatogenic Variation?
The somatogenic or somatic variation affects the somatic body cells of an organism. Since somatic cells are affected, it is not inheritable. Somatogenic variation is due to the external influences upon the body of an organism. This type of variation does not pass into the next generation. Upon the death of the organism, this variation ends. Somatic variation is also called acquired characters or modifications as individuals get these characters during their lifetime.
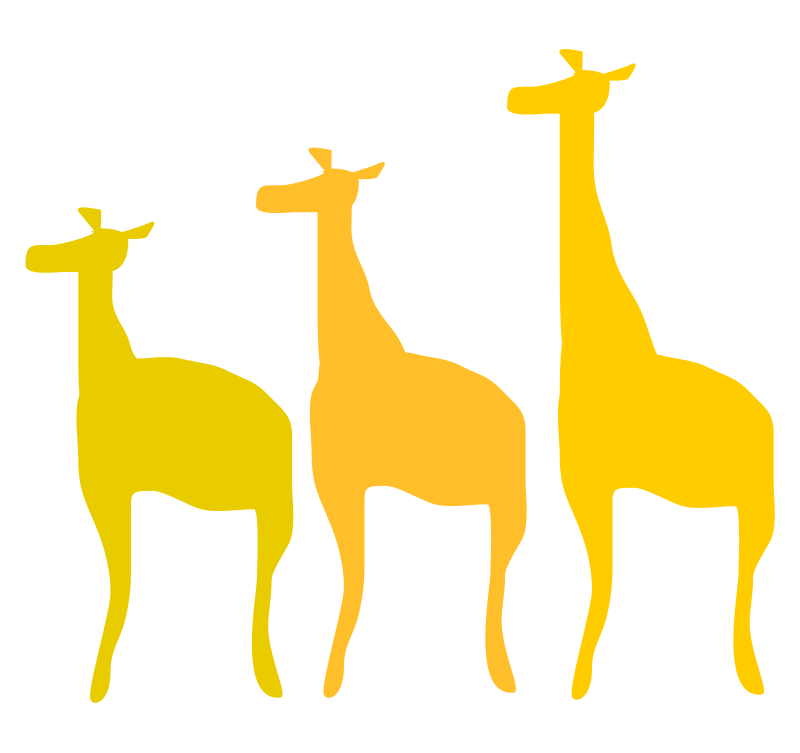

Figure 01: Somatogenic Variation
Generally, somatogenic variation occurs due to three factors: environment, use and disuse of organs, and conscious effort. Some of the environmental factors that cause somatogenic variation are medium, light, temperature, nutrition, wind, water and supply. Different changes in phenotype in response to different environmental factors are called phenotype plasticity. Moreover, a specific phenotype that is developed in response to a particular ecological condition is known as ecophenotype. Somatogenic variation in higher animals occurs mainly due to the use and disuse of organs. For example, organs that are put to continuous use develop more while the organs that are used less develop a little. Furthermore, a somatogenic variation that is due to conscious efforts is seen only in intelligent animals. Some examples of conscious efforts are training some pets, receiving education, mutilations in pets, slim bodies, long necks, etc.
What is Blastogenic Variation?
The blastogenic or germinal variation affects the germ cells of an organism. Therefore, this type of variation is inheritable. Blastogenic variation can be already present in ancestors or can be suddenly formed. Blastogenic variation is of two types: continuous or discontinuous.
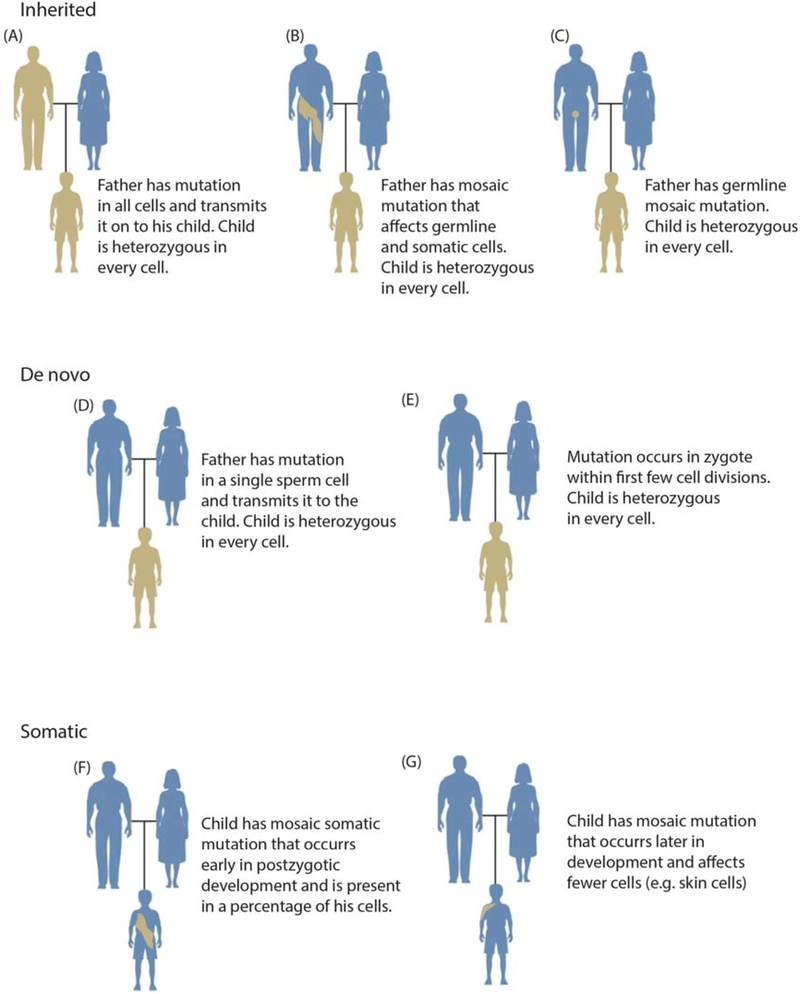
Figure 02: Blastogenic variation
Continuous blastogenic variation is of quantitative characteristics. Continuous blastogenic variation is already present in the organism. It occurs due to reasons such as chance separation of chromosomes at gamete formation, crossing over of chromosomes at meiosis and chance combination of chromosomes during fertilization, etc. Discontinuous blastogenic variation is defined as sudden, unpredictable, inheritable departures from the normal without any intermediate stage. Moreover, discontinuous blastogenic variation can occur due to various reasons such as chromosome aberrations like deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation, change in chromosome numbers like aneuploidy, polyploidy and change in gene structure and expression like addition, deletion, or change of nucleotides.
What are the Similarities Between Somatogenic and Blastogenic Variation?
- Somatogenic and blastogenic variations are two types of variations according to cells affected in an organism.
- Both variations bring out phenotypic changes in an organism.
- These variations can give extra advantages for the survival of the organism.
- They both affect the body of an organism.
What is the Difference Between Somatogenic and Blastogenic Variation?
The somatogenic variation affects somatic body cells of an organism and is not inheritable, while blastogenic variation affects germ cells of an organism and is inheritable. So, this is the key difference between somatogenic and blastogenic variation. Furthermore, somatogenic variation occurs during the life span of an individual, while blastogenic variation occurs during the gametogenesis in parents.
The below infographic lists the differences between somatogenic and blastogenic variation in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Somatogenic vs Blastogenic Variation
Variations can be found in all characters. Therefore, no two individuals are similar due to these variations. Somatogenic and blastogenic variations are two types of variations. The somatogenic variation affects the somatic body cells of an organism, and it is not inheritable. On the other hand, blastogenic variation affects the germ cells of an organism, and it is inheritable. Thus, this is the difference between somatogenic and blastogenic variation.
Reference:
1. “Types of variations, Biology” Experts Mind.
2. “What Are Blastogenic Variations?” Lifeeasy Biology: Questions and Answers.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Principe variation” By I, Toony (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Mutation inherited, de novo, somatic” By Donald Freed, Eric L. Stevens, and Jonathan Pevsner – Freed, Donald; Stevens, Eric; Pevsner, Jonathan (2014-12-11). “Somatic Mosaicism in the Human Genome”. Genes. 5 (4): 1064–1094. doi:10.3390/genes5041064. ISSN 2073-4425. PMC 4276927. PMID 25513881. (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyspqaZpKS0prrInGSappRir62t0q2moJ2enrBuwsCroJqsmaS7cA%3D%3D