The key difference between lamina propria and muscularis propria is that lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms a part of the moist linings known as the mucosa, while muscularis propria is a layer of smooth muscle adjacent to the submucosa that lines the gastrointestinal tract in the body.
The gastrointestinal wall of the gastrointestinal tract normally has four layers of specialized tissues. From the inner cavity of the gut to outwards, they are known as mucosa (epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosae), submucosa, muscular layer (muscularis propria), and serosa or adventitia.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Lamina Propria
3. What is Muscularis Propria
4. Similarities – Lamina Propria and Muscularis Propria
5. Lamina Propria vs Muscularis Propria in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Lamina Propria vs Muscularis Propria
What is Lamina Propria?
Lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that is a part of the moist linings known as mucosa lining the gastrointestinal tract in the body. In addition to the gastrointestinal tract, lamina propria lines other tubes in the body, including the respiratory tract and urogenital tract. It is a thin layer of loose or areolar connective tissue that lies beneath the epithelium. Together with epithelium and basement membrane, it makes up mucosa. It is a characteristic component of the mucosa. Lamina propria is also known as mucosa’s own special layer. Therefore, the term mucosa or mucous membrane refers to the combination of epithelium and the lamina propria.
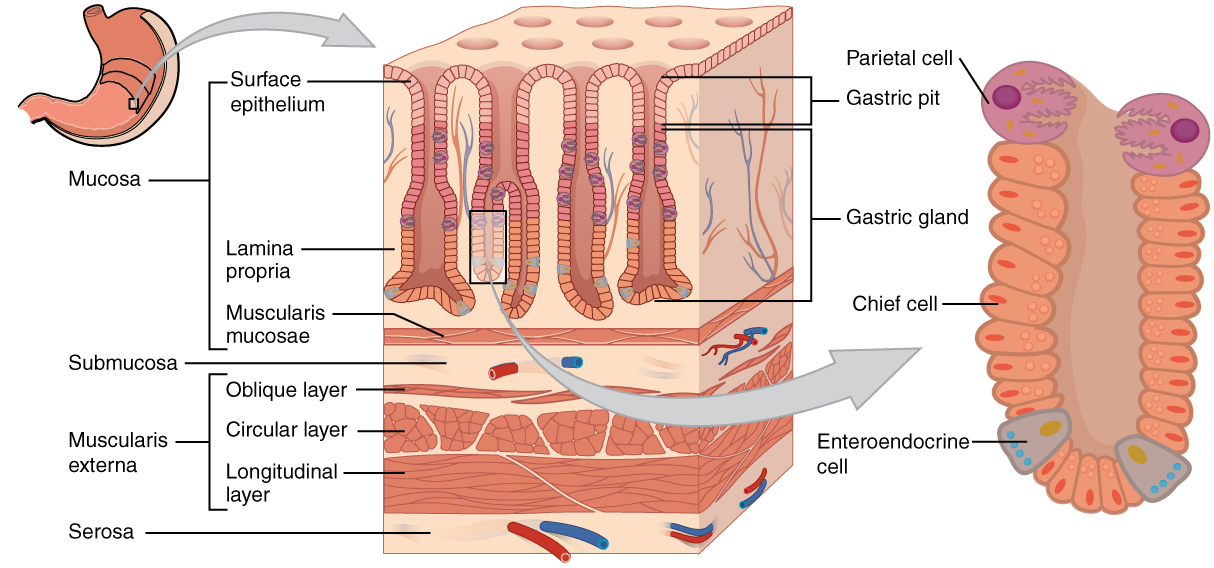
Figure 01: Lamina Propria
The connective tissue of the lamina propria is loose and usually rich in cells. The cells of the lamina propria are variable and may include fibroblasts, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, eosinophilic leukocytes, and mast cells. Moreover, lamina propria provides support and nutrition to the epithelium as well. It also helps the binding of the epithelium to the underlying tissue. Furthermore, irregularities in the connective tissue surface like papillae found in the tongue increase the area of contact of the lamina propria and epithelium.
What is Muscularis Propria?
Muscularis propria is a layer of smooth muscles adjacent to the submucosa that lines the gastrointestinal tract in the body. It is also known as the muscular coat, muscular fibers, muscularis layer, or muscularis externa. Muscularis propria usually has two layers of smooth muscle: inner and “circular”, outer and “longitudinal.” However, there are some exceptions to this pattern. In the stomach and vas deferens, there are three layers in muscularis propria. In the upper esophagus, a part of externa is a skeletal muscle rather than a smooth muscle. In the ureter, the smooth muscle orientation is opposite of the GI tract. There is an inner longitudinal and outer circular layer in muscularis propria. The inner layer of the muscularis propria forms two sphincters at two locations in the gastrointestinal tract. In the pylorus of the stomach, it forms the pyloric sphincter, and in the anal canal, it forms the internal anal sphincter.
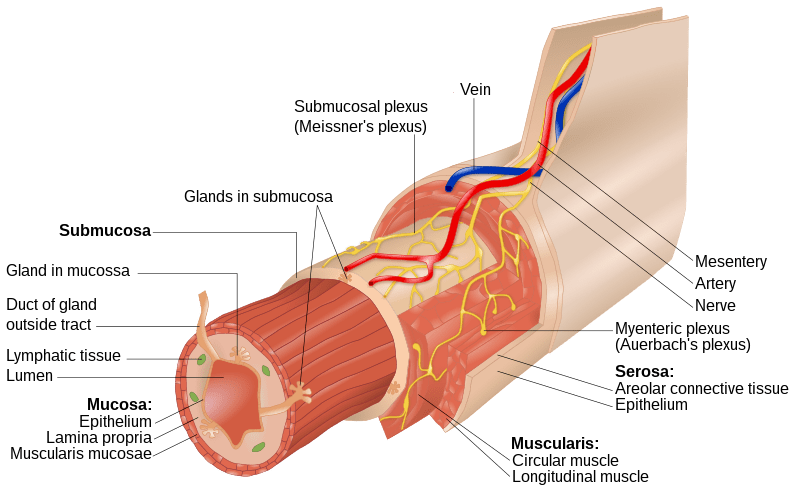
Figure 02: Muscularis Propria
Muscularis propria is responsible for the peristaltic movements and segmental contractions in the alimentary canal. The Auerbach’s nerve plexus is found between longitudinal and circular muscle layers of muscularis propria that start muscle contractions to initiate peristalsis.
What are the Similarities Between Lamina Propria and Muscularis Propria?
- Lamina propria and muscularis propria are two important layers in the gastrointestinal tract.
- They cover most types of tissues that are exposed to the external environment.
- Both layers can also be found in other tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract and urogenital tract.
- Both layers fulfil specialized functions.
What is the Difference Between Lamina Propria and Muscularis Propria?
Lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract, while muscularis propria is a layer of smooth muscles which lies adjacent to the submucosa of the gastrointestinal tract. Thus, this is the key difference between lamina propria and muscularis propria. Furthermore, lamina propria has one thin layer of connective tissue, while muscularis propria has two layers of circular and longitudinal smooth muscles.
The below infographic presents the differences between lamina propria and muscularis propria in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Lamina Propria vs Muscularis Propria
Lamina propria and muscularis propria are two important layers in the gastrointestinal tract. They can also be found in other tubes in the body, especially in the respiratory tract and urogenital tract. Lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms a part of the mucosa. Muscularis propria is a layer of smooth muscles adjacent to the submucosa that lines the gastrointestinal tract of the body. So, this is the key difference between lamina propria and muscularis propria.
Reference:
1. “Lamina Propria.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
2. Paxton, Steve, et al. “The Leeds Histology Guide.” Home: The Histology Guide.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Layers of the GI Tract english” By Goran tek-en (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “2415 Histology of StomachN” By OpenStax College – Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site, Jun 19, 2013. (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoylmKahnpZ6sb7OqamimV2Wu6V5zK6qnK2clr%2Bqv4ypqaioop6ucA%3D%3D