The key difference between Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae is that Haemophilus influenzae is a gammaproteobacterium that requires both hermin (factor X) and NAD+ (factor V) for its growth, while Haemophilus parainfluenzae is a gammaproteobacterium that requires only NAD+ (factor V) for its growth.
Haemophilus is a genus of gram-negative, pleomorphic and coccobacilli bacteria. This genus belongs to the family Pasteurellaceae. These species inhabit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, mouth, vagina, and intestinal tract. All members of this genus are either aerobic or facultative anaerobic. This genus has both commensal and pathogenic species. Some of the well-known species in this genus are Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Haemophilus ducreyi, Haemophilus haemolyticus and Haemophilus aegyptius. H. influenzae and H. parainfluenzae are two pathogenic species of this genus.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Haemophilus Influenzae
3. What is Haemophilus Parainfluenzae
4. Similarities – Haemophilus Influenzae and Haemophilus Parainfluenzae
5. Haemophilus Influenzae vs Haemophilus Parainfluenzae in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Haemophilus Influenzae vs Haemophilus Parainfluenzae
What is Haemophilus Influenzae?
Haemophilus influenzae is a gammaproteobacterium that requires both hermin (factor X) and NAD+ (factor V) for its growth. It is a gram-negative, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic bacterium. H. influenzae is a capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. This bacterium was described by Richard Pfeiffer in 1892 during an influenza pandemic. This bacterial species was the first free-living organism to have its entire genome sequenced. In 1930, H. influenzae was divided into two types of strains: unencapsulated and encapsulated. Encapsulated strains were classified into six groups based on their capsular antigens: a, b, c, d, e, f. Encapsulated strains are also known as typable strains. Unencapsulated strains are termed as non-typable (NTHi) because they lack capsular serotypes. However, they can be classified through multilocus sequence typing.
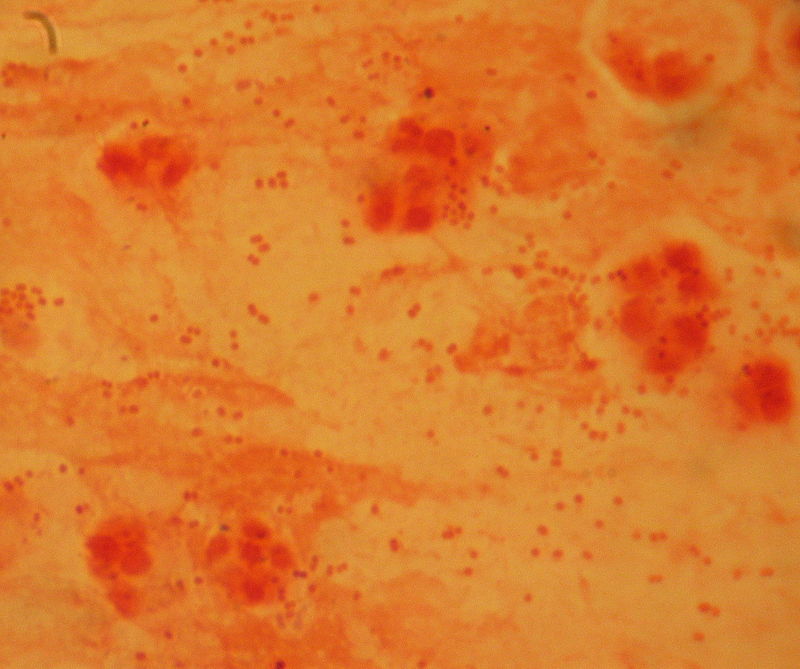
Figure 01: Haemophilus influenzae
H. influenzae type b (Hib) is a lethal strain that causes bacteremia, pneumonia, epiglottitis, acute bacterial meningitis, cellulitis, osteomyelitis and infectious arthritis. Antibiotics such as cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ampicillin, sulbactam, cephalosporin, macrolides, and fluoroquinolones are effective against H. influenzae. Moreover, infections that are caused by encapsulated strains of H. influenzae are greatly reduced by the Hib vaccine.
What is Haemophilus Parainfluenzae?
Haemophilus parainfluenzae is a gammaproteobacterium that requires only NAD+ (factor V) for its growth. It is also a gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic coccobacillus. It is a part of the HACEK group that causes 3% of infective endocarditis cases. HACEK organisms are a group of fastidious gram-negative bacteria. They are an unusual cause of infective endocarditis. HACEK group include different genera such Haemophilus, Aggregatibacter, Cardiobacterium, Eikenella and Kingella, etc. Moreover, H. parainfluenzae is an opportunistic pathogen that has been associated with endocarditis, bronchitis, conjunctivitis, pneumonia, otitis, abscesses, and genital tract infections. H. parainfluenzae biotypes I and II are capable of natural genetic transformation. Most of the isolates are sensitive to ampicillin. Moreover, some strains produce beta-lactamases.
Similarities Between Haemophilus Influenzae and Haemophilus Parainfluenzae
- influenzae and H. parainfluenzae are two pathogenic species of the genus Haemophilus.
- Both species are gammaproteobacteria.
- They belong to the family Pasteurellaceae.
- These bacteria are gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, coccobacilli.
- Both species are pathogenic.
- They have a single chromosome.
Difference Between Haemophilus Influenzae and Haemophilus Parainfluenzae
H.influenzae is a gammaproteobacterium that requires both hermin (factor X) and NAD+ (factor V) for its growth. In contrast, H. parainfluenzae is a gammaproteobacterium that requires only NAD+ (factor V) for its growth. So, this is the key difference between Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Furthermore, H. influenzae grows on chocolate agar but not on blood agar, while H. parainfluenzae grows on blood agar.
The below infographic lists the differences between Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Haemophilus Influenzae vs Haemophilus Parainfluenzae
Haemophilus is a genus of gram negative, pleomorphic and coccobacilli bacteria. These bacteria are gammaproteobacteria. This genus has both commensal and pathogenic species. Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae are two pathogenic species of the genus Haemophilus. Haemophilus influenzae requires both hermin (factor X) and NAD+ (factor V) for its growth. But Haemophilus parainfluenzae requires only NAD+ (factor V) for its growth. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae.
Reference:
1. Musher, Daniel M. “Haemophilus Species.” Medical Microbiology. 4th Edition., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 1 Jan. 1996.
2. “HaemophilusParainfluenzae.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Haemophilus influenzae Gram” By Bobjgalindo – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyhmJ6ln6W1qrjUrGSippahwqa62ZqcZpmemXqprcSmpqmgmaHCtHnPmqmaoZ6bubaxzbOYnmc%3D