The key difference between dialysis and CRRT is that dialysis is a process carried out for a time period of three to four hours, whereas CRRT is a slower and continuous process that takes more than 24-hours.
Kidneys usually filter blood, remove harmful wastes and excess fluid by turning them into urine to pass out of the body as an excretory product. When kidneys fail, an electrolyte imbalance takes place in the body where wastes, toxins, salts, and extra water build up within the body. Dialysis and CRRT (continuous renal replacement therapy) are two processes that play an important role in keeping the body in balance during kidney failure. Such processes help to keep safe levels of chemicals, remove toxic wastes and excess fluid, and also help to control blood pressure in the body.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Dialysis
3. What is CRRT
4. Similarities – Dialysis and CRRT
5. Dialysis vs CRRT in Tabular Form
6. Summary – Dialysis and CRRT
What is Dialysis?
Dialysis is a procedure carried out to remove excess fluids and waste products from the blood when kidneys do not function properly. Dialysis diverts blood to a machine to clean and purify. This process takes about 3 – 4 hours. Dialysis is mainly done in the presence of chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. The presence of waste products and excess fluids are toxic to the body as they cause various symptoms and may eventually be fatal. The severity of kidney failure decides the time period of dialysis. If kidney failure is temporary, the dialysis process ends once the kidneys recover. During a critical situation where kidney transplants are required, the dialysis process continues until a suitable donor becomes available. If the kidney transplant is not suitable during a critical situation, dialysis continues for the rest of the life.
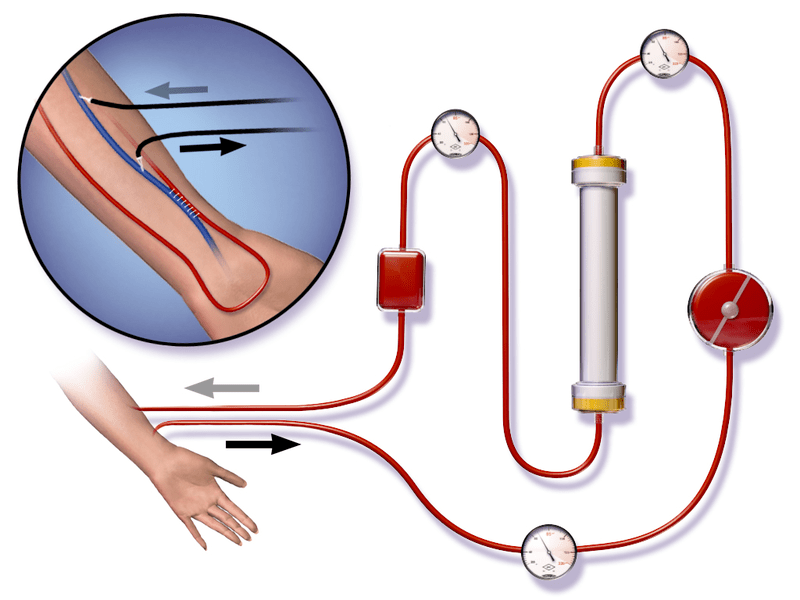
Figure 01: Dialysis Process
There are two types of dialysis: hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. Hemodialysis is the most common type of dialysis. During this process, a tube is attached to a needle in the arm, and blood passes along the tube. Initially, blood enters an external machine through a tube that filters before passing through the needle in the arm. Hemolysis dialysis is usually done three days per week, and each process lasts approximately four hours. Peritoneal dialysis is slightly different. Rather than a filtering machine, this process uses the inside lining of the abdomen called the peritoneum to filter. The peritoneum contains tiny blood vessels, and they act as a filtering unit. In this procedure, a small cut is made near the abdominal area, and a thin tube is inserted into the cavity. This is left permanently. The wastes and fluid drain to a bag, and fresh liquid replaces every 30 – 40 minutes, approximately four times a day.
What is CRRT (Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy)?
Continuous renal replacement therapy or CRRT is a 24-hour non-stop dialysis process that supports patients with kidney failure. During the CRRT therapy, blood passes through a special filter that removes excess fluid and uremic toxins and returns purified blood to the body. This is a slow process that takes over a period of 24-hours. It is a special and unique feature of CRRT. Slow continuous removal of fluid and toxins enables intravascular water refiling from tissues, and this minimizes the negative impact on hemodynamic stability. The slow and continuous process transfers the solutes from the tissues to blood and enables the removal of uremic toxins and fluid in the blood.
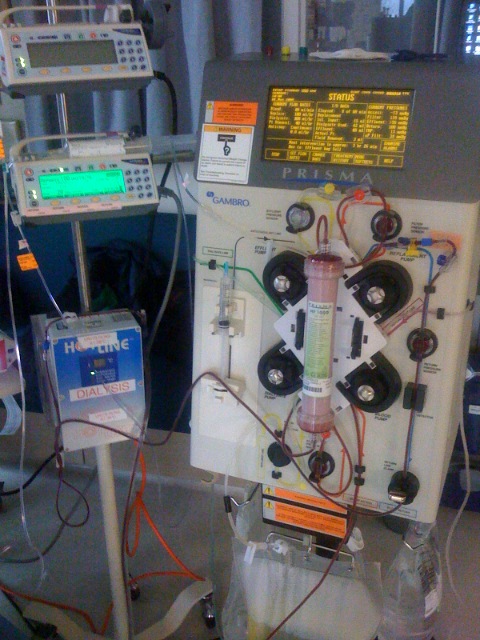
Figure 02: CRRT Dialysis Machine
CRRT contains a highly permeable hemofilter that has the capacity to remove solutes with high molecular weight. It also helps to maintain homeostasis, including fluid balance, acid-base balance, electrolytic balance, and colloid osmotic pressure within the body. CRRT therapy is often used for patients with acute renal failure and with complications such as multiple organ failure, cardiac imperfections, acute pancreatitis, or liver failure. CRRT requires special anticoagulation to prevent the dialysis circuit from clotting.
What are the Similarities Between Dialysis and CRRT?
- Dialysis and CRRT are carried out using a venous catheter and a semi-permeable membrane.
- Both have the same principle of removing excess fluid and toxic waste from blood during the condition of kidney failure.
- Moreover, the techniques require hospitalization.
- Immunocompromised patients may have severe effects upon both dialysis and CRRT.
What is the Difference Between Dialysis and CRRT?
Dialysis completes within three to four hours, whereas CRRT runs continuously for approximately 24 hours. This is the key difference between dialysis and CRRT. Patients can tolerate CRRT therapy better than dialysis. Moreover, dialysis removes large amounts of fluids and wastes in a shorter period of time, while CRRT removes fluids and wastes at a lower and steady rate.
The below infographic presents the differences between dialysis and CRRT in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Dialysis vs CRRT
Dialysis and CRRT are two processes that play an important role in keeping the body in balance during kidney failure. Dialysis is done three to four hours at a time, whereas CRRT is continuously done for approximately 24 hours. So, this is the key difference between dialysis and CRRT. Dialysis is a procedure to remove excess fluids and waste products from the blood when kidneys do not function properly. CRRT is a continuous or non-stop dialysis process that supports patients with kidney failure. Both processes divert blood through a special filter which removes excess fluid and uremic toxins and return purified blood to the body.
Reference:
1. “Overview – Dialysis.” NHS Choices, NHS.
2. “Understanding Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) in COVID-19 Management.” Baxter.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Blausen 0313 Dialysis” By Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014” WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436. – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Emma’s CRRT (dialysis)” By Matt Kowalczyk (CC BY-NC 2.0) via Flickr
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoydoJqkqai2tHnAp5tmm6KnwXA%3D