The key difference between combinatorial and parallel synthesis is that combinatorial synthesis use mixtures of compounds for reactions, whereas parallel synthesis uses an individual compound for reactions.
Combinatorial synthesis is the chemical synthesis method that can make it possible to prepare a large number of compounds in a single process. Parallel synthesis is an important technique that can be used to accelerate the discovery of new compounds and to screen for optimal process conditions.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Combinatorial Synthesis
3. What is Parallel Synthesis
4. Combinatorial vs Parallel Synthesis in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Combinatorial vs Parallel Synthesis
What is Combinatorial Synthesis?
Combinatorial synthesis is the chemical synthesis method that enables preparing a large number of compounds in a single process. The term “large number” in this context might mean tens to thousands or even millions of compounds. We can synthesize these compound libraries as mixtures, sets of individual compounds, or chemical structures. These structures are generated by computer software. The branch that studies combinatorial synthesis is known as combinatorial chemistry. It can be useful for the synthesis of small molecules such as peptides.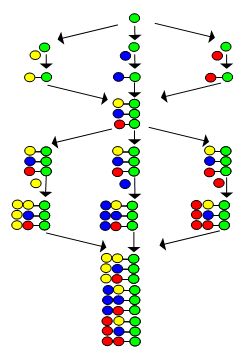
The pattern of synthesis of molecules using combinatorial synthesis can quickly lead to a large number of molecules. For instance, if there is a molecule having three points of diversity known as R1, R2, and R3, it can generate NR1 x NR2 x NR3 possible structures. The NR1, NR2, and NR3 are the numbers of different substituents utilized.
Basically, combinatorial chemistry involves the preparation of libraries of a very large number of compounds; then, the libraries can be used to identify useful components. Different industries have identified the uses of the combinatorial synthesis method by the 1990s. However, we can trace the origins of this method to the 1960s.
What is Parallel Synthesis?
Parallel synthesis is an important technique that can be used in accelerating the discovery of new compounds and in screening for optimal process conditions. It is a time-saving method and allows us to differentiate compounds by running multiple experiments simultaneously.
This technique is important for the pharmaceutical industry. We can use this method to discover and develop potential drug candidates. E.g. parallel synthesis enables us to synthesize libraries with diverse chemical structures which are screened for potential biological activity. Applications of this technique are in different scales, which include lead generation, lead optimization, and screening for optimal reaction conditions.
What is the Difference Between Combinatorial and Parallel Synthesis?
Combinatorial synthesis is the chemical synthesis method that can make it possible to prepare a large number of compounds in a single process. Parallel synthesis is an important technique that can be used in accelerating the discovery of new compounds and in screening for optimal process conditions. The key difference between combinatorial and parallel synthesis is that combinatorial synthesis use mixtures of compounds for reactions, whereas parallel synthesis uses an individual compound for reactions. Moreover, combinatorial synthesis uses a split synthesis method, whereas parallel synthesis uses one-bead-one-compound method.
The below infographic presents the differences between combinatorial and parallel synthesis in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Combinatorial vs Parallel Synthesis
Combinatorial and parallel synthesis are important synthetic techniques that are mainly useful in the pharmaceutical industry. The key difference between combinatorial and parallel synthesis is that combinatorial synthesis use mixtures of compounds for reactions, whereas parallel synthesis uses an individual compound for reactions.
Reference:
1. Mettler-Toledo International Inc. “Parallel Synthesis.” Screening of Reaction Conditions | Technology, 26 Aug. 2020.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Split-mix synthesis” By SynthAr – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “ZnO Nanostructure Synthesis” By Penguin54335 – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoycpqaamaOutbvRopilZZGjsW68wKuYpaSVoXq0xc2tn56rmah8