The key difference between biotin and collagen is that biotin is vitamin B7, which cannot be produced by the body, whereas collagen is a fibrous protein produced by the body and occurs in bones, muscles, tendons, and skin.
Biotin and collagen are important substances that occur in the human body. These compounds have many important applications in our body and in many other organisms.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Biotin
3. What is Collagen
4. Biotin vs Collagen in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Biotin vs Collagen
What is Biotin?
Biotins is vitamin B7 that is involved in many metabolic processes in both humans and microorganisms in relation to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name biotin comes from the Greek words “bios” and the suffix “-in” and has the meaning “to live.”
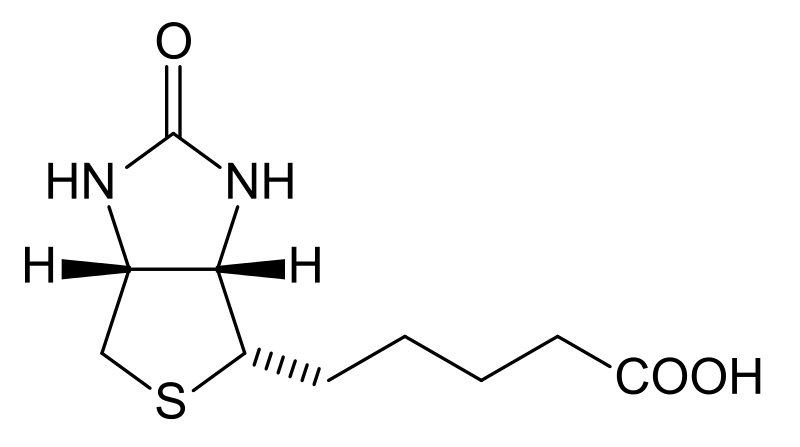
Figure 01: The Chemical Structure of Biotin
Biotin appears as white crystalline needles. The chemical formula of this compound is C10H16N2O3S. We can classify it as a heterocyclic compound having a sulfur-containing ring (ureido ring and tetrahydrothiophene ring). Biotin can act as a coenzyme for five carboxylase enzymes involved in the digestion of carbohydrates, production of fatty acids, and gluconeogenesis.
There are many different sources of biotin: chicken liver, beef liver, eggs, egg white, egg yolk, salmon, pork chop, turkey breast, tuna, peanuts, sunflower seeds, avocado, corn, strawberry, broccoli, cheese, milk, oatmeal, French fries, beer, etc.
There are significant uses of biotin in biotechnology. The major applications include the isolation of proteins and non-proteins for biochemical assays. For example, egg-derived avidin can strongly bind with biotin along with a comparatively high dissociation constant.
Deficiency of biotin can occur in two forms as primary deficiency and subclinical deficiency. Primary deficiency happens due to too little amount of biotin in the food. It is a rare condition because many food sources contain biotin. Subclinical deficiency, however, can cause some mild symptoms such as hair thinning, brittle fingernails, skin rash on the face, etc.
What is Collagen?
Collagen is a structural protein we can find in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues in our body. It is a main component in the connective tissue. In addition, collagen is the most abundant protein in mammals. The content of collagen in our body protein content can vary from 25-35%. Moreover, collagen contains amino acids that are linked to each other, forming a triple helix of elongated fibril known as the collagen helix. The connective tissues where we can find collagen in high content include cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin.
The degree of mineralization can determine the rigidity of collagen tissues. For example, bones are rigid, and tendons are compliant. Further, collagen can be found abundantly in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and dentin in teeth.
There are some medical uses of collagen, which include cardiac applications, cosmetic surgery, bone grafts, tissue regeneration, reconstructive surgical uses, wound healing, etc. Furthermore, it has applications in research interests such as cell cultures.
There are some collagen-related diseases such as Osteogenesis imperfect, infantile cortical hyperostosis, Caffey’s disease, collagenopathy, Alport syndrome, etc. Therefore, it has many applications in medical purposes to avoid these diseases. Besides, it is useful in the cosmetic industry for cosmetic surgery and burns surgery. Commonly, it has a wide application in the food industry as the collagen casing in sausages.

Figure 02: Collagen Casing of Sausages
The major sources of collagen include fish, chicken, egg white, berries, citrus fruit, white tea, garlic, red and yellow vegetables, etc.
What is the Difference Between Biotin and Collagen?
Biotin is important in cell growth and fatty acid metabolism, while collagen can provide us with structural support and strength. The key difference between biotin and collagen is that biotin is vitamin B7, which cannot be produced by the body, whereas collagen is a fibrous protein produced by the body and occurs in bones, muscles, tendons, and skin.
The below infographic presents the differences between biotin and collagen in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – Biotin vs Collagen
Biotins is vitamin B7 that is involved in many metabolic processes in both humans and microorganisms in relation to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. Collagen is a structural protein that we can find in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues in our body. The key difference between biotin and collagen is that biotin is vitamin B7, which cannot be produced by the body, whereas collagen is a fibrous protein produced by the body and occurs in bones, muscles, tendons, and skin.
Reference:
1. Catlett, Tess. “Biotin for Hair Growth.” Healthline, Healthline Media.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Biotin structure” By Mysid – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Beretta Salami and Collagen Casing” By Ll1324 – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyboKismaN6orrDZpqopJyWtKa6jg%3D%3D