The key difference between ATP and GTP is that ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate made up of adenine nitrogenous base, sugar ribose, and triphosphate, while GTP is a nucleoside triphosphate made up of guanine nitrogenous base, sugar ribose, and triphosphate.
A nucleoside triphosphate is a molecule comprised of a nitrogenous base, 5-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and three phosphate groups. The nitrogenous base is bound to the 5-carbon sugar. The three phosphate groups are bound to the sugar as well. Nucleoside triphosphate is an example of nucleotide. They are the molecular precursors of both DNA and RNA. These nucleoside triphosphates also serve as a source of energy for the reaction in the cells. Moreover, they are involved in the signalling pathways. Therefore, ATP and GTP are two types of nucleoside triphosphates that are very important for cellular function.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is ATP
3. What is GTP
4. Similarities – ATP and GTP
5. ATP vs GTP in Tabular Form
6. Summary – ATP vs GTP
What is ATP?
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is a nucleoside triphosphate that consists of adenine nitrogenous base, sugar ribose and triphosphate. ATP is the primary energy currency of the biological cell. It is produced in various metabolic pathways in the cell as an end product. It is primarily produced during cellular respiration and photosynthesis. A specific enzyme called ATP synthase catalyzes the synthesis of ATP in the cell. Usually, ATP synthase carries out the synthesis of ATP from ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and phosphate with an electrochemical gradient generated by the pumping of protons. The pumping of protons is through either the inner mitochondrial membrane (in cellular respiration) or the thylakoid membrane (in photosynthesis). This electrochemical gradient is highly important because ATP production is energetically unfavourable.
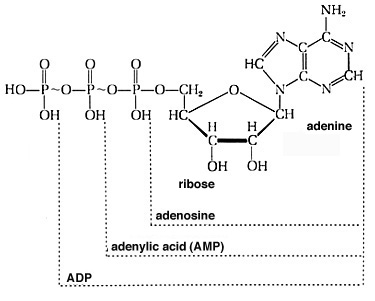
Figure 01: ATP
When ATP is consumed in the metabolic processes, it converts either to ADP again or to AMP (adenosine monophosphate). Furthermore, ATP hydrolysis to ADP and Pi is energetically favourable. The hydrolysis produces 30.5 k/J amount of energy. In the cell, ATP hydrolysis is often coupled with unfavourable reactions in order to provide the energy for those reactions to proceed.
What is GTP?
GTP (guanosine triphosphate) is a nucleoside triphosphate that comprises a guanine nitrogenous base, sugar ribose and triphosphate. GTP is occasionally used for energy coupling in a similar manner as ATP. It is essential for signal transduction, especially with G proteins. G proteins are normally coupled with a cell membrane-bound receptor. This whole complex is known as G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). G proteins can bind either to GDP (guanosine diphosphate) or GTP. When G proteins bind to GDP, they are inactive.
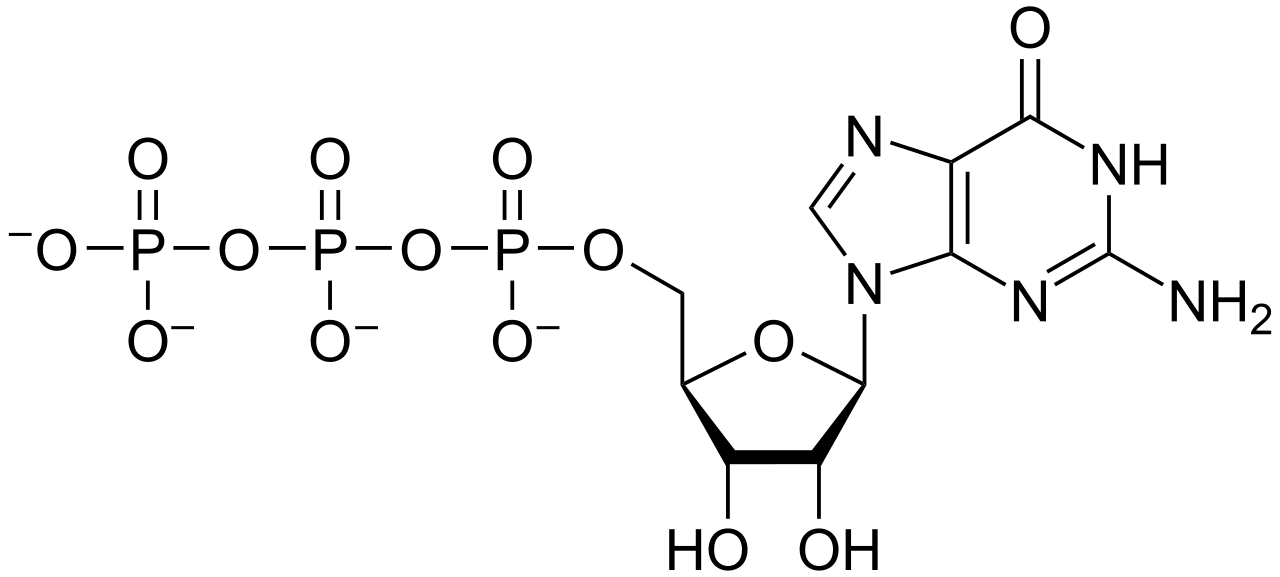
Figure 02: GTP
When a ligand binds to the GPCR complex, an allosteric change in the G protein is triggered. This causes GDP to leave and GTP to replace. Moreover, GTP activates the alpha subunit of the G protein, which causes the dissociation from the G protein and acts as a downstream effector molecule in the cell. GTP is synthesized as a by-product in the cell normally through processes such as the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinate. Succinyl CoA synthetase catalyzes this particular reaction in the Kreb cycle.
What are the Similarities Between ATP and GTP?
- ATP and GTP are two types of nucleoside triphosphates that are very important for cellular function.
- Both are organic molecules.
- These molecules have sugar ribose group and triphosphate group commonly in their structure.
- They also contain purine bases.
- Both molecules play the role of the source of energy or an activator of substrates in metabolic reactions.
- These are the molecular precursors of DNA and RNA.
What is the Difference Between ATP and GTP?
ATP contains adenine nitrogenous base, sugar ribose and triphosphate, while GTP contains guanine nitrogenous base, sugar ribose and triphosphate. So, this is the key difference between ATP and GTP. Furthermore, ATP is synthesized in the cell from ADP and phosphate by a specific enzyme called ATP synthase, while GTP is synthesized as a by-product in the cell through processes such as the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinate by a specific enzyme called succinyl CoA synthetase.
The below infographic lists the differences between ATP and GTP in tabular form for side by side comparison.
Summary – ATP vs GTP
ATP and GTP are two types of nucleoside triphosphates that are very important for cellular function. ATP comprises adenine base, sugar ribose and triphosphate, while GTP comprises guanine base, sugar ribose and triphosphate. ATP is the energy currency in the cell, while GTP participates in different signalling pathways and is essential in signal transduction. Thus, this summarizes the difference between ATP and GTP.
Reference:
1. “Adenosine Triphosphate.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
2. “Guanosine Triphosphate.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Structure of ATP” By Vtvu – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “GTP chemical structure” By Hbf878 – Own work (CC0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue9ahmK1lmah6tbTEZpuinpaav6a6wp5km52krLKmuoyaq6llkaOxbrPTqWY%3D