Key Difference – Transformants vs Recombinants
Recombination and transformation are two crucial steps in genetic engineering, where the characteristics of an organism are deliberately modified by manipulating its genetic material. Recombination is a process in which foreign DNA is incorporated into a vector genome and recombinant DNA molecule is formed. Transformation is the next step in which recombinant molecule is entered into the host organism. The host cell or the organism facilitates expression of the recombinant molecule. The key difference between transformants and recombinants is that transformants are the cells or the organisms which take recombinant molecule inside and facilitate expression while recombinants are the vectors which allow insertion of the foreign DNA into its genome and transport into host transformants for expression.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Transformants
3. What are Recombinants
4. Side by Side Comparison – Transformants vs Recombinants
5. Summary
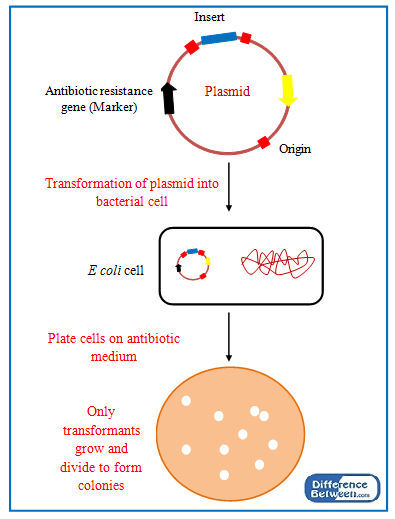
What are Transformants?
Transformants are the cells or the organisms in which recombinant DNA is taken up for the expression. Bacteria are commonly used as host organisms in genetic engineering since they are easy to grow, multiply and handle under laboratory conditions and transformation process is easy compared to other organisms. The most popular host bacterium used in genetic engineering is bacterium E coli.
During the transformation process, host cells are induced to take up the recombinants. However, some host cells do not take up recombinant molecules. They are known as nontransformants and the cells which contain recombinant DNA molecules inside are known as transformants. Selection of transformants from nontransformants is done using selectable markers in molecular biology. Selectable markers are inserted into vector genome together with the DNA insert. Commonly used selectable markers are antibiotic resistant genes. Marker genes facilitate the differentiation of transformants and continue the process. After the transformation process, bacterium is grown in an antibiotic-containing medium. Only the transformants are capable of growing on that medium since they possess the recombinants inside.
Once the recombinant DNA molecule is transformed inside the host organism, the foreign DNA can either be integrated into host cell genome or remain nonintegrated in the cytoplasm. However, the expression and the replication of the foreign DNA occur in the host organism and produce the desired result from the process.
What are Recombinants?
A recombinant is an organism or a cell which possesses recombined genome containing foreign DNA. Recombinants are a result of the genetic engineering process. They are artificially constructed in vitro by inserting the genes of interest and modifying the genome. Often bacterial plasmids and bacteriophages act as recombinants in genetic engineering. It has chimera of different DNAs. Recombinant DNA molecule carries foreign DNA to the host organism and makes it express and form the desired product.
Recombinant molecules are constructed using restriction endonucleases and DNA ligases. The desired DNA fragment is separated from the original organism and inserted into the vector to make the recombinant for transformation. Cutting of the gene of interest and opening of the vector organism should be done using the same restriction enzyme to create compatible sticky ends to join them together. Once the foreign DNA is incorporated into vector genome, it is known as recombinant or the recombinant DNA molecule.
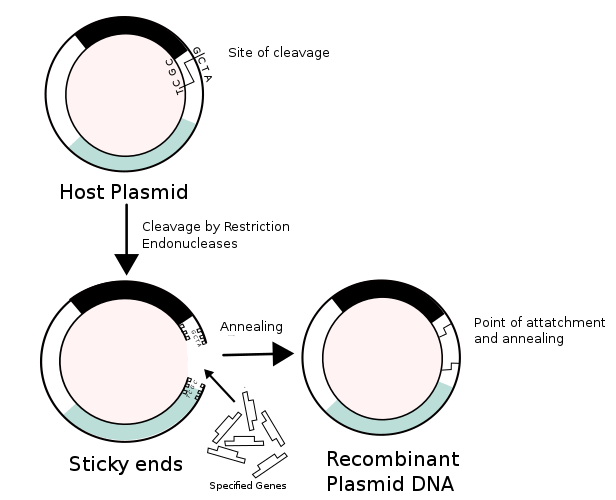
Figure 02: Recombinant DNA
What is the difference between Transformants and Recombinants?
Transformants vs Recombinants | |
| Transformants are the cells which have recombinant DNA molecule inside. | Recombinants are the carrier molecules which have foreign DNA inserted into own genome. |
| Expression of Foreign DNA | |
| They are the host cells which are able to express the recombinant DNA. | They should be able to self-replicate within the host organism. |
| Selection | |
| Cells which can be easily grown and multiply are selected as host cells. | They must be easily extractable and should contain selectable markers. |
Summary – Transformants vs Recombinants
Transformants are the cells or organisms with recombinant DNA molecules inside them. Recombinants are the organisms or the cells which have undergone genetic recombination and have foreign DNA within their genomes. Bacterial cells are often used as host cells for transformation and plasmids and bacteriophages are often used as vectors in recombinant DNA technology. This is the difference between transformants and recombinants.
References:
1. Griffiths, Anthony JF. “Making recombinant DNA.” An Introduction to Genetic Analysis. 7th edition. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 08 Apr. 2017
2. Cooper, Geoffrey M. “Recombinant DNA.” The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 08 Apr. 2017
Image Courtesy:
1. “Recombinant formation of plasmids” By Minestrone Soup at English Wikipedia (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau27A0ZqlrJ6fp7qiutOsZJqmlGLDtHnRnpqopZKeu6K606xm