The key difference between RIA and ELISA is that radioimmunoassay (RIA) is an immunoassay technique that uses radioisotopes to detect antigen-antibody complexes while enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunoassay technique that uses enzymes to detect antigen-antibody complexes.
Detection of specific proteins such as antigens is extremely important in disease diagnosis. Therefore, RIA and ELISA are two immunoassay techniques used in laboratories to detect specific proteins rapidly, especially antigens. Generally, a specific antibody binds to the target antigen and forms a visible complex known as precipitin. These antibody and antigen complexes can be identified through different techniques. The technique of detecting the antigen-antibody complex by using radioisotopes is known as RIA, and the technique of detecting the antigen-antibody complex by using enzymes is known as ELISA.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is RIA
3. What is ELISA
4. Similarities Between RIA and ELISA
5. Side by Side Comparison – RIA vs ELISA in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is RIA?
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) is an immunoassay technique that detects antigen and antibody complexes using radioisotopes. Rosalyn Sussman Yalow developed this technique in 1960 with the help of Solomon Berson. For this remarkable discovery, Rosalyn Sussman Yalow won the Nobel Prize for medicine in 1977. Typically, in radioimmunoassay, a known quantity of an antigen is first made radioactive This technique frequently uses gamma-radioactive isotopes of iodine, called 125-I, to label antigens. These radioisotopes normally attach to the tyrosine amino acid of the antigen. Then the radiolabelled antigen is mixed with antibody. As a result, the radiolabelled antigen and antibody specifically bind to one another.
Later, a sample of serum that contains an unknown quantity of the same antigen is added. This causes the unlabelled antigen from the serum to compete with the radiolabelled antigen for antibody binding sites. As the concentration of unlabelled antigen increases, more of it binds to the antibody, displacing the radiolabelled variant. Thus, it reduces the ratio of antibody-bound radiolabelled antigen to free radiolabelled antigen. At the end of the procedure, the bound antigens are separated out. Ultimately, the radioactivity of free antigens in the remaining supernatant is measured using a gamma counter.
What is ELISA?
ELISA is an immunoassay technique that detects antigen and antibody complexes by using enzymes. It is a biochemical analytical assay first described by Engvall and Perlmann in 1971. In most simple forms of ELISA techniques, antigens of the patient sample are attached to a solid surface. Then a matching antibody is applied over the surface, so it can bind to the antigen.
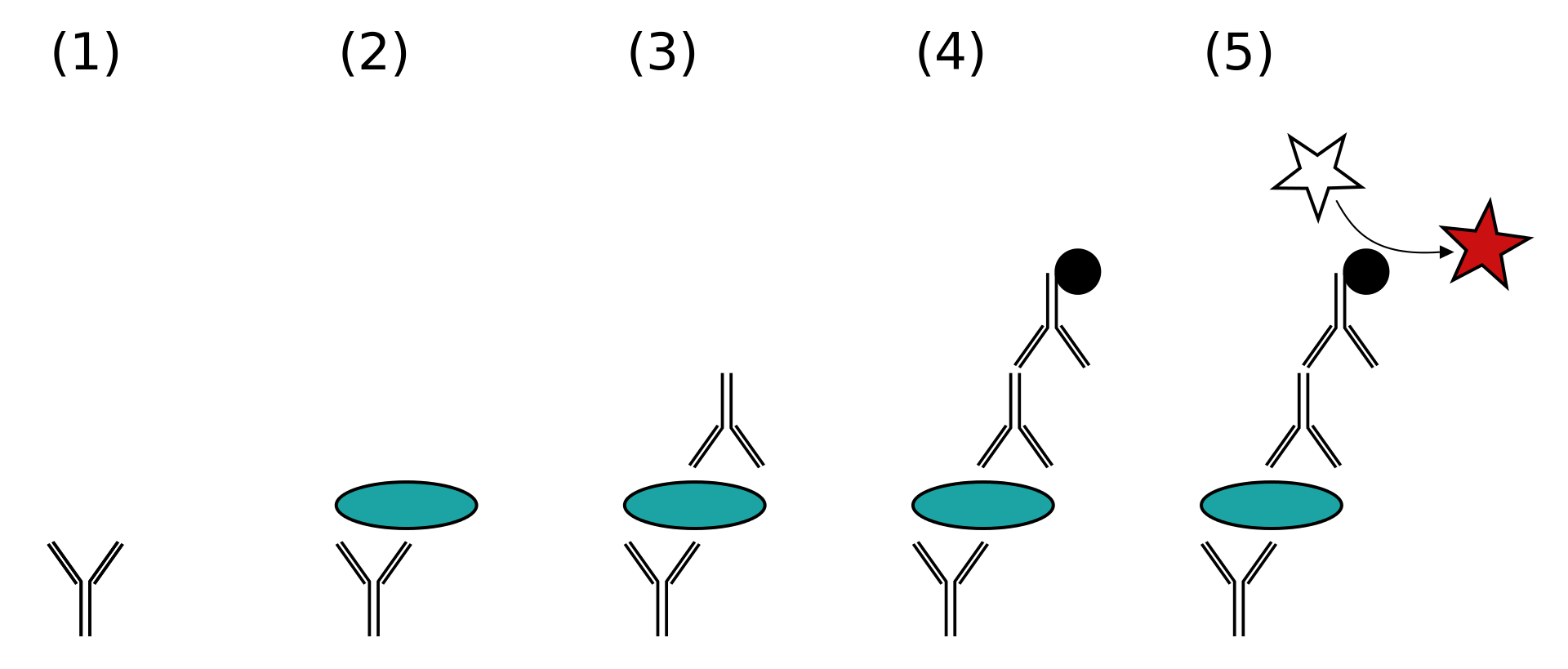
Figure 01: ELISA
This particular antibody is linked to an enzyme. Later, any unbound antibodies are removed by washing with detergent. In the final step of this technique, the enzyme’s substrate is added. If there is a proper binding of antigen and antibody, the subsequent reaction produces a detectable colour signal, most commonly a colour change.
What are the Similarities Between RIA and ELISA?
- RIA and ELISA are immunoassay techniques.
- Both techniques possess antigen and antibody complex formation.
- These techniques can be used to detect unknown proteins in samples.
- They are both used in diseases diagnosis in laboratories.
- Both are highly specific and sensitive techniques.
What is the Difference Between RIA and ELISA?
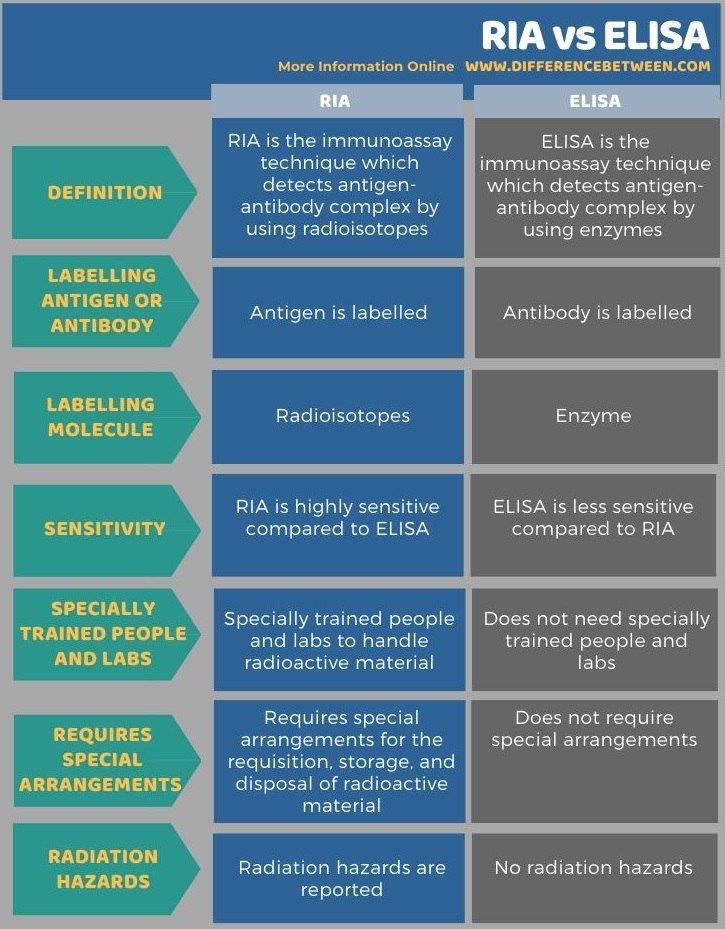
RIA is an immunoassay technique for the detection of the antigen-antibody complex by using radioisotopes. ELISA is an immunoassay technique for the detection of the antigen-antibody complex by using enzymes. So, this is the key difference between RIA and ELISA. Moreover, in the RIA technique, the antigen is labelled, but in ELISA, the antibody is labelled. Furthermore, in the RIA technique, labelling molecules are radioisotopes, whereas, in ELISA, labelling molecules are enzymes. Thus, this is another difference between RIA and ELISA.
The below infographic shows more differences between RIA and ELISA in tabular form.
Summary – RIA vs ELISA
Immunoassays play a very important role in various bioanalytical settings, such as clinical diagnostics, biopharmaceutical analysis, environmental monitoring, biosecurity, and food testing. Since the 1960s, a wide range of immunoassays has been developed. RIA and ELISA are both immunoassay techniques. RIA is an immunoassay technique for detecting antigen-antibody complex by using radioisotopes. ELISA is an immunoassay technique for detecting antigen-antibody complex by using enzymes. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between RIA and ELISA.
Reference:
1. Dutta, Dr. Sanchari Sinha. “What Are Immunoassays?” News, 20 Dec. 2018, Available here.
2. Cox, Karen L. “Immunoassay Methods.” Assay Guidance Manual [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 8 July 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “ELISA-sandwich” By Jeffrey M. Vinocur (CC BY 2.5) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26%2ByJpkmqaUYrKttdKaZg%3D%3D