The key difference between proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans is that proteoglycans are organic compounds containing a protein bound to a mucopolysaccharide whereas glycosaminoglycans are mucopolysaccharides containing a number of disaccharide repeating units.
Proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans are biochemical compounds that can be found in our body. These are very large compounds containing a large number of atoms per molecule.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Proteoglycans
3. What are Glycosaminoglycans
4. Side by Side Comparison – Proteoglycans vs Glycosaminoglycans in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What are Proteoglycans?
Proteoglycans are compounds containing a protein and a mucopolysaccharide in combination with each other. Therefore, these compounds are named as proteins, and they are highly glycosylated. The protein in this molecule is called the “core protein”. Generally, the core protein contains one or more glycosaminoglycan units attached to it. This attachment is a covalent bond, and it occurs via a serine residue. Here, one glycosaminoglycan is attached through a tetrasaccharide bridge (four monosaccharide units form the bridge). The glycosaminoglycan molecules occur as long, linear polymer chains. Moreover, these polymer chains are negatively charged chemical species due to the presence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. Usually, we can observe the presence of proteoglycans in connective tissues of the human body.
Figure 01: Protein Structure
Furthermore, proteoglycans can be classified based on the type of glycosaminoglycan present in the molecule and the size of the proteoglycan. For example, there are small and large proteoglycans when they are categorized depending on the size of the molecule and some classes of proteoglycan classified based on the glycosaminoglycan include keratan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, etc.
When considering the functions of proteoglycans in the human body, we can find them as major components in the animal’s extracellular matrix. And, they form cartilages upon the combination with collagen and involves in binding cations and water with cells.
What are Glycosaminoglycans?
Glycosaminoglycans are a type of mucopolysaccharide containing a large number of disaccharide units combined with each other in a linear structure. Usually, these repeating units contain an amino sugar, uronic sugar, and galactose (except for keratan). Glycosaminoglycans are important in the human body as lubricants and shock absorbers.
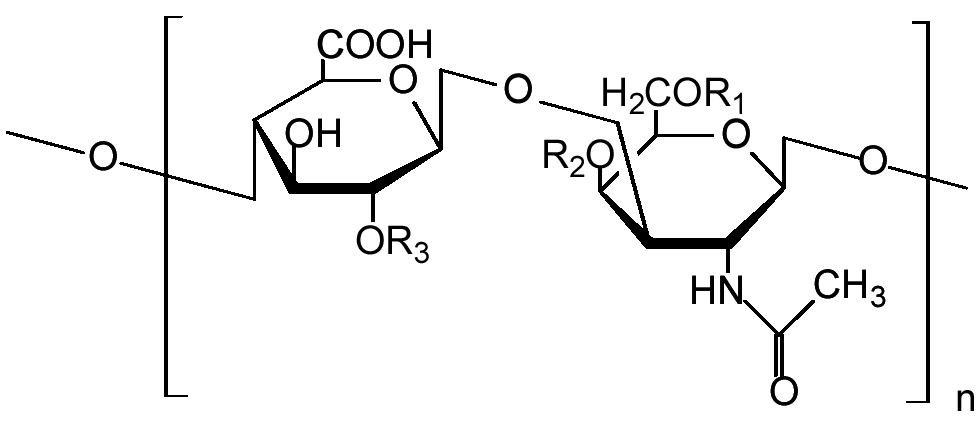
Figure 02: Disaccharide Repeating Unit
Since the production of glycosaminoglycans is not governed by a template as for proteins, these molecules vary greatly in disaccharide construction and sulfation. This production process is constantly altered by enzyme action. We can classify glycosaminoglycans into four major groups as heparin, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, and hyaluronic acid.
When considering the functions of glycosaminoglycans, they are important in interacting with heparin-binding proteins for wound repair, maintenance of tissue hydration, binding cells together (hyaluronic acid), lubricating joints, help maintain the shape of eyeballs, etc.
What is the Difference Between Proteoglycans and Glycosaminoglycans?
Proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans are biochemical compounds that can be found in our body. These are very large compounds containing a large number of atoms per molecule. The key difference between proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans is that proteoglycans are organic compounds containing a protein bound to a mucopolysaccharide whereas glycosaminoglycans are mucopolysaccharides containing a number of disaccharide repeating units.
Moreover, another significant difference between proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans is their functions. The proteoglycans are major components in the animal’s extracellular matrix. And, they form cartilages upon the combination with collagen and involve in binding cations and water with cells. Meanwhile, glycosaminoglycans are important in interacting with heparin-binding proteins for wound repair, maintenance of tissue hydration, binding cells together (hyaluronic acid), lubricating joints, help maintain the shape of eyeballs, etc.
Below infographic tabulates the differences between proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans.
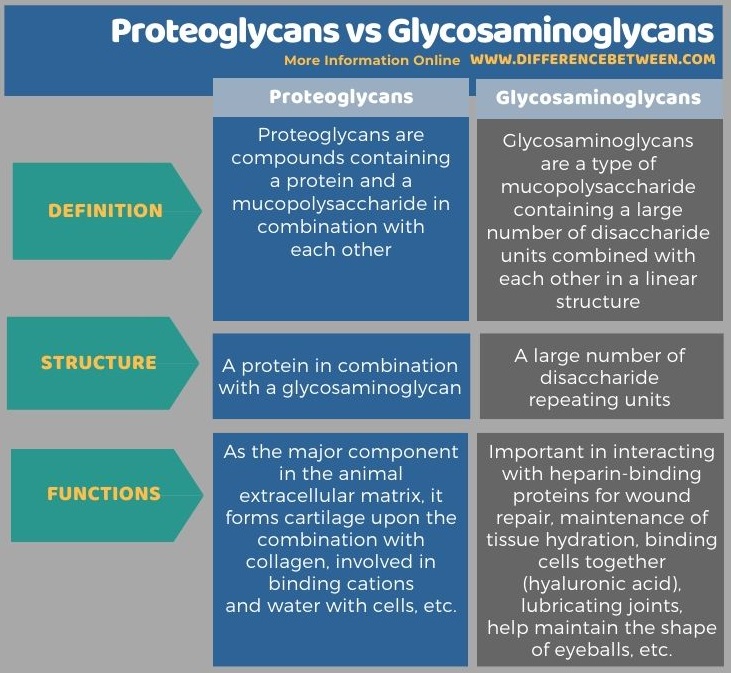
Summary – Proteoglycans vs Glycosaminoglycans
Proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans are biochemical compounds that can be found in our body. These are very large compounds containing a large number of atoms per molecule. The key difference between proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans is that proteoglycans are organic compounds containing a protein bound to a mucopolysaccharide whereas glycosaminoglycans are mucopolysaccharides containing a number of disaccharide repeating units.
Reference:
1. “Proteoglycans.” Proteoglycans – an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics, Available here.
2. “Glycosaminoglycan.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 17 Apr. 2020, Available here.
3. “Glycosaminoglycans.” Glycosaminoglycans – an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “PBB Protein ACAN image” By www.pdb.org (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Chondroitin Sulfate Structure NTP” By The original uploader was Prithason at English Wikipedia.(Original text: National Toxicology Program) – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons.(Original text: ntp.niehs.nih.gov), (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau2680airnqeXocakrc2sZJqmlGK0rcXCqKqapZmjvKi42JyYp6tf