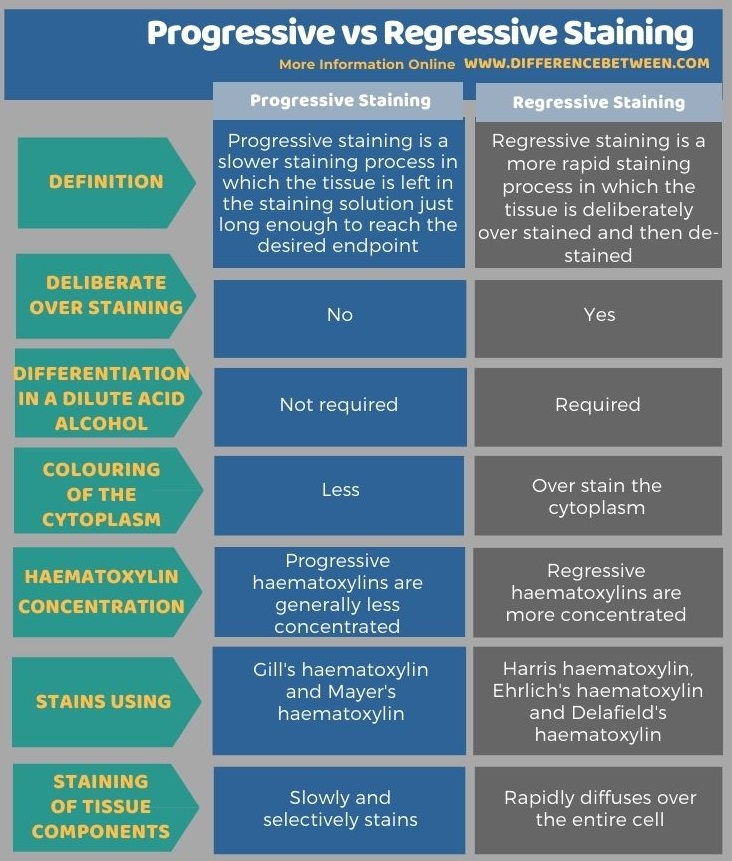
The key difference between progressive and regressive staining is that in progressive staining, the tissue is left in the staining solution just long enough to reach the desired endpoint while in regressive staining, the tissue is deliberately left for over staining until the dye saturates all tissue elements and then de-stained.
Staining is a technique which highlights and differentiates tissue components and makes it feasible to observe under the microscope. H and E staining is the general tissue staining procedure that is most commonly used in histology. It uses haematoxylin and eosin (counterstain). Nuclear staining using haematoxylin can be accomplished with progressive or regressive staining techniques. Some haematoxylin formulations are used in progressive staining. Mayer’s haematoxylin is one example. Progressive stains have a low haematoxylin concentration. Hence, they slowly and selectively stain the chromatin. Some other formulations are used in regressive staining. Harris haematoxylin is used in regressive staining. Regressive stains have a high concentration of haematoxylin; hence, the stain rapidly diffuses over the entire cell.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Progressive Staining
3. What is Regressive Staining
4. Similarities Between Progressive and Regressive Staining
5. Side by Side Comparison – Progressive vs Regressive Staining in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Progressive Staining?
Progressive staining is a technique that allows the tissue in the staining solution just long enough to reach the desired endpoint. Therefore, frequent monitoring of stain quality is needed to determine the completion of staining. The staining intensity is controlled by the immersing time.
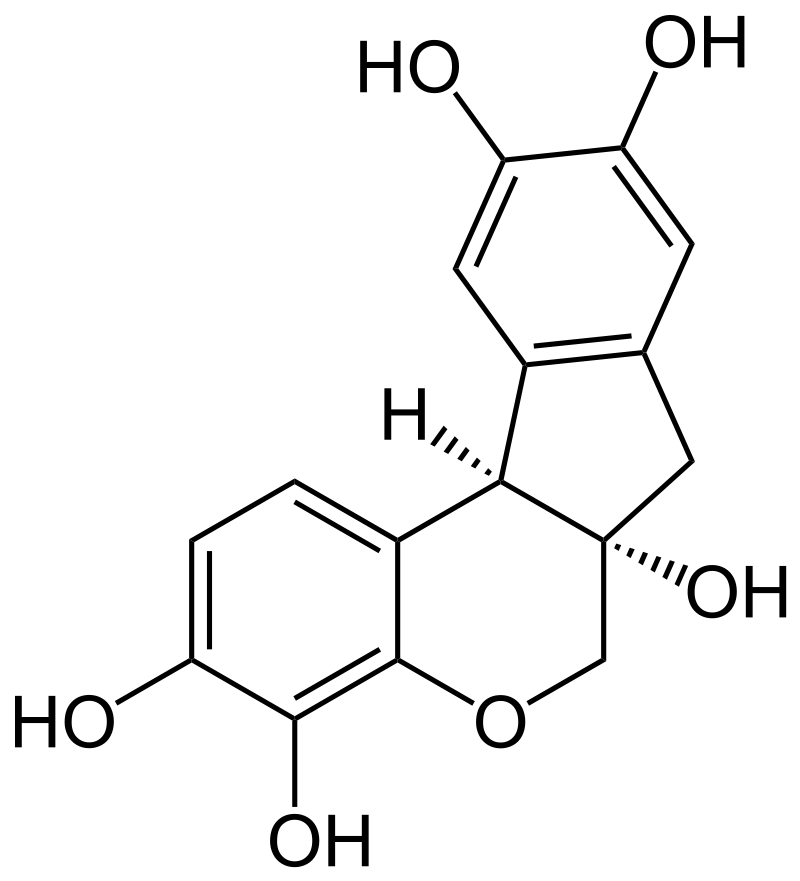
Figure 01: Haematoxylin Structure
Gill’s haematoxylin and Mayer’s haematoxylin are progressive in nature. For these two haematoxylings, a staining time of 5-10 minutes is used commonly in progressive staining. Generally, progressive haematoxylins are less concentrated. Hence, they slowly and selectively stain chromatin. In progressive staining, haematoxylin primarily stains the chromatin to the desired intensity. Thus, it does not require differentiation in dilute acid alcohol to pull out the excess stain.
What is Regressive Staining?
Regressive staining is a more rapid staining technique in which the tissue is deliberately over stained until the dye saturates all tissue components. Then the tissue is selectively de-stained until it reaches the correct endpoint. De-staining step is called differentiation. Differentiation is done to remove excess stains. Usually, it is done using dilute acid alcohol.
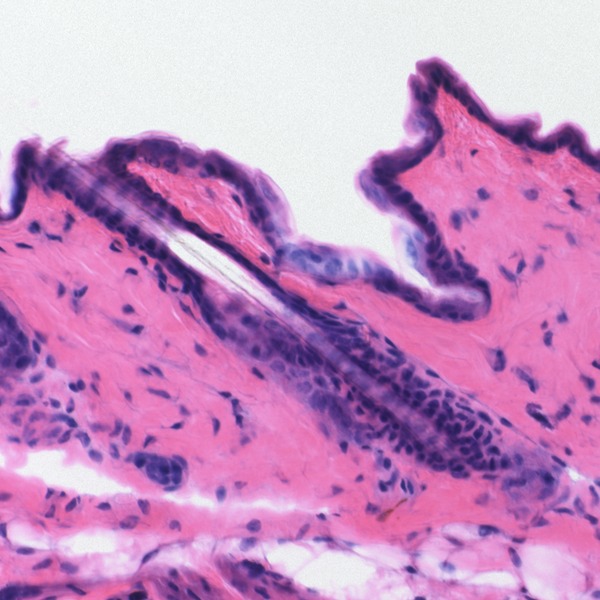
Figure 02: H and E Staining
Harris haematoxylin is the popularly used type of haematoxylin. Ehrlich’s and Delafield’s haematoxylins are also using in regressive staining. Regressive stains have a high concentration of haematoxylin. Hence, they rapidly diffuse the entire cell and over stain the chromatin and cytoplasm. Regressive staining is preferred when very clear differentiation of tissue elements is required.
What are the Similarities Between Progressive and Regressive Staining?
- Progressive and regressive staining are two types of staining techniques.
- Both use the dye called haematoxylin.
What is the Difference Between Progressive and Regressive Staining?
Progressive staining is a slower staining process in which the tissue is left in the staining solution just long enough to reach the desired endpoint. In contrast, regressive staining is a more rapid staining process in which the tissue is deliberately over stained and then de-stained. So, this is the key difference between progressive and regressive staining.
Moreover, another significant difference between progressive and regressive staining is that progressive staining does not require an additional step called differentiation, while regressive staining requires differentiation in order to remove excess stains. Besides, progressive stains have a low concentration of haematoxylins, while regressive stains have a higher concentration of haematoxylins.
The below infographic tabulates more differences between progressive and regressive staining.
Summary – Progressive vs Regressive Staining
Progressive staining is a slow staining technique in which the tissue is left in the staining solution just long enough to reach the endpoint. Therefore, over staining is not done is progressive staining. In contrast, regressive staining is a more rapid staining technique in which the tissue is over stained and then de-stained. Progressive staining does not require differentiation (removal of excess stain) while regressive staining requires differentiation in dilute acid alcohol in order to remove excess stain. Progressive stains generally have a low concentration of haematoxylins while regressive stains have more concentration of haematoxylins. Thus, this summarizes the difference between progressive and regressive staining.
Reference:
1. “Routine H &Amp; E”. Slideshare.Net, 2020, Available here.
2. “Haematoxylin – the Story of the Blues.” Viapath, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Hämatoxylin” By NEUROtiker (talk) – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “H&E Eby Loyola University Chicago” By Jonathan Eby – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau2680aieq52jqLa3sYyapZ1lopq0s7HSrKCvnV2owaK1zaKloGc%3D