Key Difference – NADH vs FADH2
A coenzyme is an organic non-protein molecule which is relatively small in size and has the ability to carry chemical groups between enzymes and act as an electron carrier. NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) and FADH2 (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) are two main coenzymes utilized in almost all biochemical pathways. They act as electron carriers and participates in oxidation-reduction reactions of reaction intermediates. NADH is a derivative of Vitamin B3 (Niacin/Nicotinamide) while FADH2 is a derivative of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin). This is the key difference between NADH and FADH2.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is NADH
3. What is FADH2
4. Similarities Between NADH and FADH2
5. Side by Side Comparison – NADH vs FADH2 in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is NADH?
NADH is synthesized from Vitamin B3 (Niacin) and is a coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5′-diphosphate coupled to adenosine 5′-phosphate. It serves as an electron carrier in many reactions by alternatively converting to its oxidized (NAD+) form and the reduced (NADH) form. The reduced NADH acts as an electron donor and oxidize to NAD+ while reducing the other compound involved in the reaction. This role of NADH is involved in the processes of glycolysis, TCA cycle and in the electron transport chain where NADH is one of the electron donors.
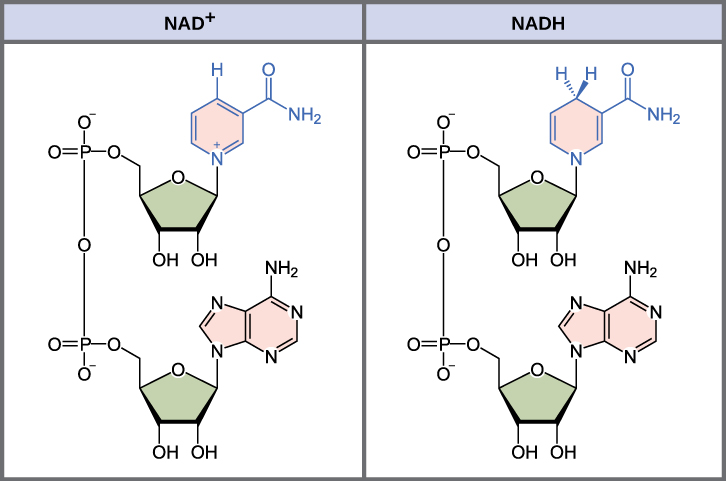
Figure 01: Structures of NADH and NAD+
The melting point of NADH is 140.0 – 142.0 °C and it can be synthesized in the body and is not an essential nutrient. But the deficiency of the essential vitamin Niacin can cause a decrease in the composition of NADH in the body. NADH is produced in the cytosol as well as in the mitochondria. The mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to NADH, and this barrier distinguishes between cytoplasmic and mitochondrial NADH stores.
In commercial applications, NADH is administered orally in order to combat fatigue as well as during energy deprived syndromes and metabolic disorders
What is FADH2?
FADH2 is synthesized from the water-soluble vitamin B2, which is also known as Riboflavin. FADH2 is the reduced form of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD).
FAD is synthesized from riboflavin and two molecules of ATP. Riboflavin is phosphorylated by ATP to produce riboflavin 5′-phosphate (also called flavin mononucleotide, FMN). FAD is then formed from FMN by the transfer of an AMP molecule from ATP.

Figure 02: Structures of FAD and FADH
FADH is involved in both carbohydrate metabolism and fatty acid metabolism. In carbohydrate metabolism, FADH is involved in harvesting high energy electron rich fuels in the TCA cycle. FADH is generated in each round of fatty acid oxidation, and the fatty acyl chain is shortened by two carbon atoms as a result of these reactions to yield Acetyl Co A. FADH acts as an electron donor in the electron transport.
What are the Similarities Between NADH and FADH2?
- NADH and FADH2 are coenzymes
- Both act as electron carriers.
- Both are nonprotein organic molecules.
- Both are derived from vitamins.
- Both are water soluble.
- Both can exist in the reduced form or oxidized form.
- Both participate in oxidation and reduction reactions and help in the transfer of electrons from one substrate to the other.
- Both coenzymes can be synthesized in the body.
- Both molecules take part in metabolic pathways which include carbohydrate, fatty acid, amino acid and nucleotide metabolism.
What is the Difference Between NADH and FADH2?
NADH vs FADH2 | |
| NADH is a coenzyme derived from vitamin B3 or niacin. | FADH2 is a coenzyme derived from Vitamin B2 or riboflavin. |
| ATP Produced | |
| NADH gives 3 ATP. | NADH gives 2 ATP. |
| Commercial Applications | |
| NADH is used as a supplement under energy deprived conditions. | This has no commercial applications. |
Summary – NADH vs FADH2
The role of NADH and FADH2 is to donate electrons to the electron transport chain and to act as an electron carrier, which carries electrons released from different metabolic pathways to the final process of energy production, i.e., the electron transport chain. They both donate electrons by providing a hydrogen molecule to the oxygen molecule to create water during the electron transport chain. Thus both NADH and FADH2 are vital in all metabolic processes. The difference between NADH and FADH2 is that NADH is a coenzyme derived from vitamin B3 or niacin whereas FADH2 is a coenzyme derived from Vitamin B2 or riboflavin.
Download PDF Version of NADH vs FADH2
You can download PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation note. Please download PDF version here Difference Between NADH and FADH2
References:
1. “FADH2.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Available here. Accessed 4 Sept. 2017.
2.“Introduction to NAD/NADH.” Introduction to NAD/NADH, Available here. Accessed 4 Sept. 2017.
3. “NADH.” National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Available here. Accessed 4 Sept. 2017.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Figure 07 01 01ab” By CNX OpenStax (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “FADH2 production by flavin reductase for HOCl generation and halogenase activity” By Jmont31 – Diagram made with ChemDraw (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau266wJ2fZpmemXq3v4yfmJ2gYmQ%3D