The key difference between mother cell and daughter cell is that the mother cell is a parent cell that subjects to cell division to produce new cells while the daughter cell is a new cell formed as a result of cell division.
In multicellular organisms, cell division is an essential process in order to produce new cells required for growth, development, and reproduction. From the existing mature cells, new cells originate as a result of two types of cell divisions; namely, mitosis and meiosis. The mature cell which is undergoing cell division is the parent cell or the mother cell while the new cells originating at the end of the cell division are daughter cells. Likewise, mitosis produces two daughter cells from a single parent cell while the meiosis produces four daughter cells from a single mother cell. Daughter cells of the mitosis are genetically identical to the mother cell while the daughter cells of the meiosis are not genetically identical to the mother cell. Instead, they contain half of the genetic material of the mother cell.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Mother Cell
3. What is Daughter Cell
4. Similarities Between Mother Cell and Daughter Cell
5. Side by Side Comparison – Mother Cell vs Daughter Cell in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Mother Cell?
Mother cell or parent cell is a mature cell that prepared for a cell division. During the cell division, mother cell undergoes different stages of cell division such as interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
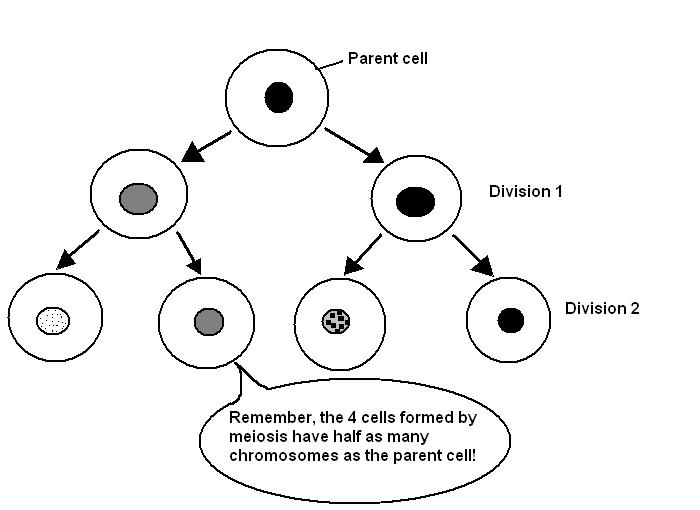
Figure 01: Parent Cell
Finally, it undergoes cytokinesis and separates into new cells. Mother cells are mostly diploid. During the growth and development, mother cells produce new cell through mitosis. During the reproduction, mother cells produce reproductive cells through meiosis.
What is Daughter Cell?
Daughter cell is a new cell produced at the end of the cell division. Daughter cells are genetically identical to the mother cell at the stage of production through mitosis. On the other hand, at the stage of production through meiosis, the daughter cells are genetically different and contain only half of the genetic material of the mother cell.
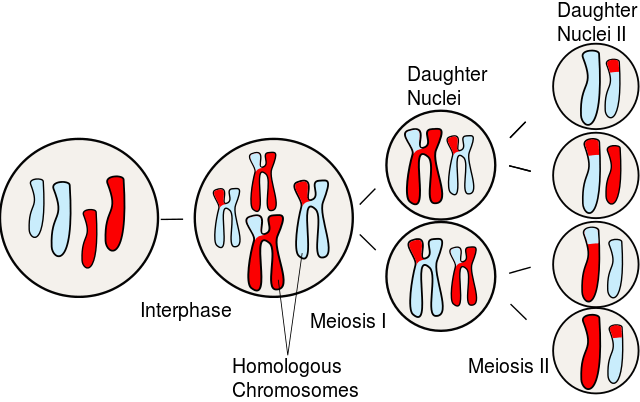
Figure 02: Daughter Cells
Mitosis produces two daughter cells from one mother cell. Meiosis produces four daughter cells from one mother cell. Daughter cells are immature by the time they originate. Hence, some remain attached to the mother cell without separating. Later, they become mature and start to work as independent individual cells.
What are the Similarities Between Mother Cell and Daughter Cell?
- Mother cell and daughter cells are visible in multi-cellular organisms.
- Both are involved in the cell division.
What is the Difference Between Mother Cell and Daughter Cell?
Mother cell and daughter cell are two types of cells identified during the cell division. Mother cell is the cell that divides into daughter cells. Daughter cells are the resulting cells of the cell division. Therefore, this is the key difference between mother cell and daughter cell. Furthermore, mother cell is a diploid cell while daughter cell can be either diploid or haploid. From one mother cell, several daughter cells are resulting. During the mitosis, from one mother cell, two daughter cells are resulting while during the meiosis, four daughter cells are resulting from one mother cell. Structurally mother cell is a mature cell while the daughter cell is an immature cell. Thus, this is another difference between mother cell and daughter cell.
Below is an infographic on the difference between mother cell and daughter cell.

Summary – Mother Cell vs Daughter Cell
Mother cell and daughter cell are two types of cells involving cell division. Mother cell is the cell that undergoes cell division while daughter cell is the cell that results. Not only one daughter cell results from one mother cell; several other cells also get formed. Two daughter cells are produced from mitosis while four daughter cells are produced from meiosis. Mother cell is a diploid cell while some daughter cells are diploid while some are haploid. Thus, this is the difference between the mother cell and daughter cell.
Reference:
1.“Phases of Mitosis.” Khan Academy, Khan Academy. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Meiosis”By Rlawson at en.wikibooks, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”MajorEventsInMeiosis” (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau265zq2fnqpdmLKtuIyapZ1llJbCqLTTnqlmm5WhuXA%3D