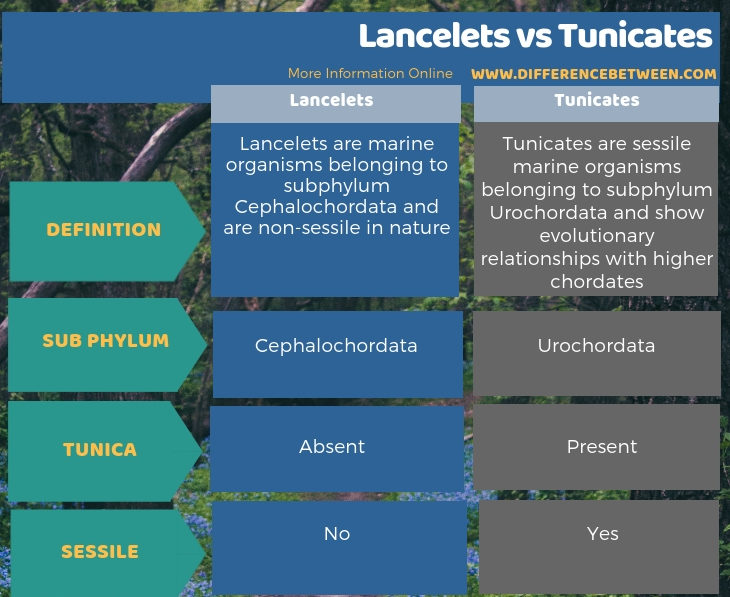
The key difference between lancelets and tunicates is that Lancelets belong to the subphylum Cephalochordata while Tunicates belong to the subphylum Urochordata.
Lancelets and Tunicates are marine organisms that belong to the phylum Chordata. They have their evolutionary and structural differences, which divide them into two subphyla. However, both represent the very primitive form of chordates.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Lancelets
3. What are Tunicates
4. Similarities Between Lancelets and Tunicates
5. Side by Side Comparison – Lancelets vs Tunicates in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Lancelets?
Lancelets are chordates. They belong to the phylum Chordata and the subphylum Cephalochordata. They are small blade-shaped marine organisms. The anatomical structure of lancelets is such that they have a slightly swollen tip on the anterior end of their dorsal nerve cord. Moreover, they do not have a fully developed brain structure. Thus, scientists suggest that the nerve cord tip is the preliminary form of the developed brain in higher chordates.
The anterior region of lancelet is elongated in shape. It consists of organ structures such as the heart and the digestive system. They expose their anterior end to filter feed themselves. They mainly feed on planktons.
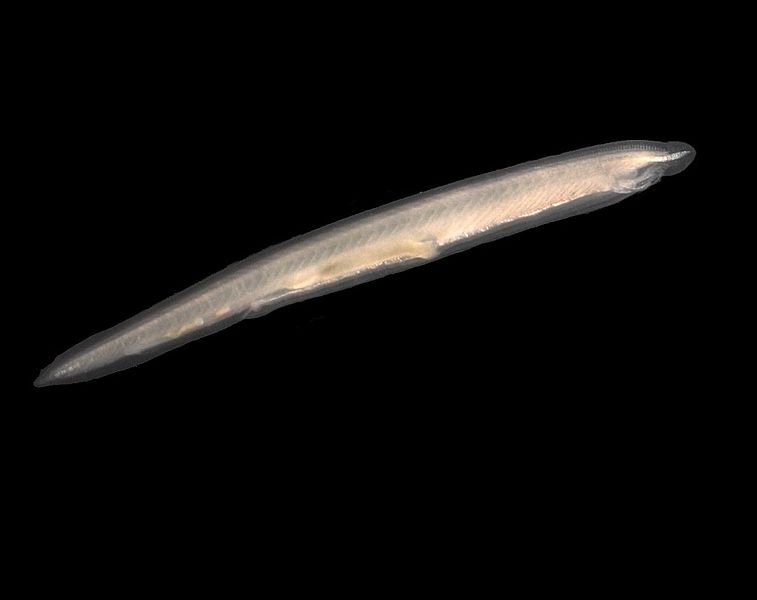

Figure 01: Lancelet
Reproduction of lancelets takes place externally through fecundation. They reproduce seasonally. Therefore, they are known as gonochoric animals. The spawning season varies between different species of lancelets.
What are Tunicates?
Tunicates are another group of chordates. But, they belong to the phylum Chordata and the subphylum Urochordata. They are all marine organisms. Moreover, they are sessile and very closely related to hagfish and jaw vertebrates. In fact, they represent the earliest forms of chordates.
Moreover, they are filter feeders and have tubular openings known as siphons to facilitate movement in the water and for their respiration. Also, they possess a notochord during their larval stages. However, they lack it in their adult stages. They are surrounded by an outer membrane known as the tunic. The tunic constitutes of carbohydrates and proteins. Moreover, it also acts as an exoskeleton for tunicates.
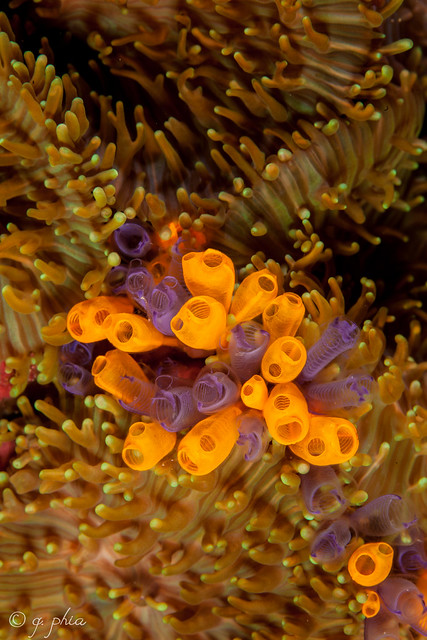

Figure 02: Tunicates
Furthermore, tunicates have a developed circulatory system with a completely developed heart. However, they do not have a developed excretory system as they lack developed kidneys. They lack a brain but have a cerebral ganglion that participates in nervous coordination. Also, they are hermaphrodites and show prominent larval stages during their life cycle.
What are the Similarities Between Lancelets and Tunicates?
- Lancelets and tunicates belong to the phylum Chordata.
- Both are marine organisms.
- They have respiratory and circulatory organs.
- Moreover, they possess a nerve cord but do not possess a brain.
- Both show larval stages.
What is the Difference Between Lancelets and Tunicates?
Lancelets and tunicates primarily differ based on their subphyla. That is; lancelets belong to the subphylum cephalochordate whereas tunicates belong to the subphylum Urochordates. So, this is the key difference between lancelets and tunicates. Moreover, they also differ based on the presence of the tunic. The tunic is characteristic only to tunicates. Therefore, this is also a significant difference between lancelets and tunicates.
Furthermore, tunicates are sessile while lancelets are not. So, this is also a difference between lancelets and tunicates.
Summary – Lancelets vs Tunicates
Lancelets and tunicates are primitive chordates. They belong to separate subphyla. In this regard, lancelets belong to the subphylum Cephalochordata while tunicates belong to the subphylum Urochordata. They are exclusively marine. Tunicates are sessile while lancelets are not sessile and resemble fish. They have a nerve cord, but they lack a developed brain. So, this is a summary of the difference between lancelets and tunicates.
Reference:
1. “Chordata – Vertebrates, Tunicates, Lancelets: Wildlife Journal Junior – Wildlife Journal Junior.” New Hampshire PBS, Available here.
2. “Chordates – Tunicates and Lancelets.” Google Sites, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “tunicates, the zoo, wakatobi, 2018” By q phia (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
2. “Branchiostoma lanceolatum” By © Hans Hillewaert (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau264wKeanqSVqcBurc2dZK2tnp6wosDErGY%3D