The key difference between herbaceous monocot and herbaceous dicot stems is that in herbaceous monocot stems, vascular bundles are scattered, while in herbaceous dicot stems, vascular bundles are organized in a ring.
Flowering plants produce flowers as their reproductive structures. There are two major groups of flowering plants as monocots and dicots. Monocots have one cotyledon, while dicots have two cotyledons. Moreover, monocots often have an adventitious root system, while dicots have a tap root system. The organization of vascular bundles inside the herbaceous stem is also different among monocots and dicots.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Herbaceous Monocot Stems
3. What are Herbaceous Dicot Stems
4. Similarities Between Herbaceous Monocot and Herbaceous Dicot Stems
5. Side by Side Comparison – Herbaceous Monocot vs Herbaceous Dicot Stems in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Herbaceous Monocot Stems?
All plants begin their development as herbaceous or non-woody organisms. In herbaceous monocot stems, the vascular bundles are scattered. Moreover, monocot stems do not have vascular cambium and cork cambium. In addition, distinct areas of pith and cortex are absent in monocot stems.
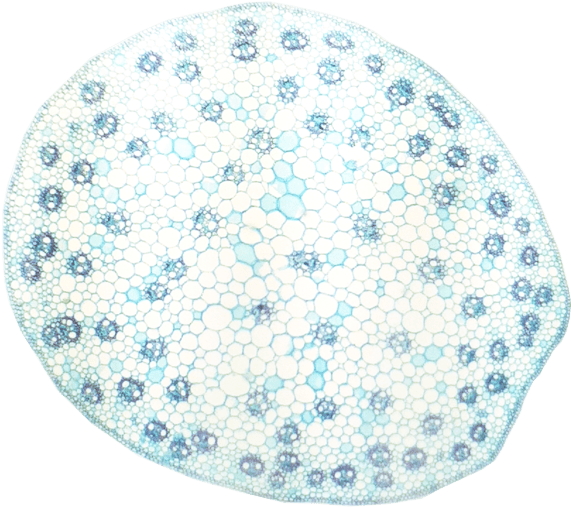
Figure 01: Herbaceous Monocot Stem
Secondary vascular tissue production is also not seen in herbaceous monocot stems. In vascular bundles, xylem is located closer to the centre of the stem while phloem is located closer to the surface.
What are Herbaceous Dicot Stems?
The vascular bundles of herbaceous dicot stems are arranged in a circle or a ring. In a vascular bundle, both xylem and phloem can be seen. The vascular cambium, which is responsible for the secondary growth in dicot stems, is located in between the xylem and phloem.

Figure 02: Herbaceous Dicot Stem
The centre area of herbaceous dicot stem is the pith composed of large, thin-walled parenchyma cells that function primarily for storage. Moreover, a distinct area of cortex is also found in the herbaceous dicot stem. Cortex is a part of the plant’s ground tissue system, containing parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma cells.
What are the Similarities Between Herbaceous Monocot and Herbaceous Dicot Stems?
- Both monocot and dicot stems have vascular bundles.
- These stems provide storage, support and conductance of water, minerals and nutrients in the plant.
- Moreover, they take part in photosynthesis as well.
What is the Difference Between Herbaceous Monocot and Herbaceous Dicot Stems?
Herbaceous monocot stems have scattered vascular bundles, while herbaceous dicot stems have vascular bundles arranged in a circular cross-section. So, this is the key difference between herbaceous monocot and herbaceous dicot stems. Moreover, monocots stems have a ground tissue instead of a distinct cortex and pith, while dicot stems have a distinct cortex and pith. Also, another difference between herbaceous monocot and herbaceous dicot stems is the presence of vascular cambium. That is; dicot stems have a vascular cambium, while monocot stems do not have a vascular cambium. Besides, vascular bundles of monocot stems are closed, while vascular bundles of dicot stems are open.
Below infographic summarizes the difference between herbaceous monocot and herbaceous dicot stems.
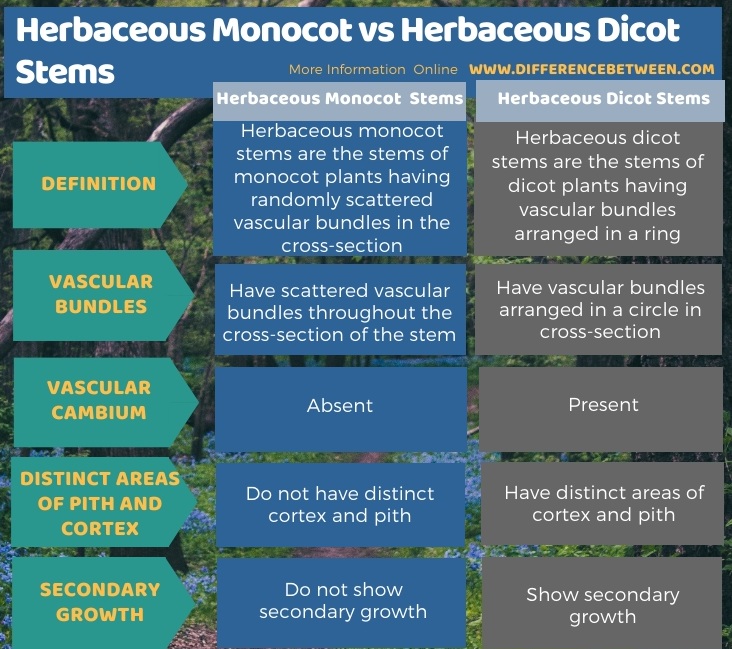
Summary – Herbaceous Monocot vs Herbaceous Dicot Stems
Herbaceous monocot stems have vascular bundles randomly distributed throughout the cross-section. In contrast, herbaceous dicot stems have vascular bundles arranged in a circle in the cross-section. Thus, this is the key difference between herbaceous monocot and dicot stems. Moreover, monocot stem does not have distinct areas of pith and cortex while dicot stems have a cortex and a pith. Also, dicot stems have a vascular cambium and show secondary growth. However, vascular cambium is absent in monocot stems, and they do not show secondary growth. So, this is the end of the discussion of the difference between herbaceous monocot and dicot stems.
Reference:
1.“Structure of Monocot Stem: Botany.” Biology Discussion, 30 Aug. 2016, Available here.
2. “Dicot Stem.” Sciencetopia, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Botana curus monocot stem 40×” By Kelvinsong – Own work (CC BY 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Herbaceous Dicot Stem: Young Helianthus” By Berkshire Community College Bioscience Image Library (Public Domain) via Flickr
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau260xKuZmpuVpMK0ecyopaibn6l6orrDZp%2BeqpKWsKa71KxknaGTpMFuv9OepKxn