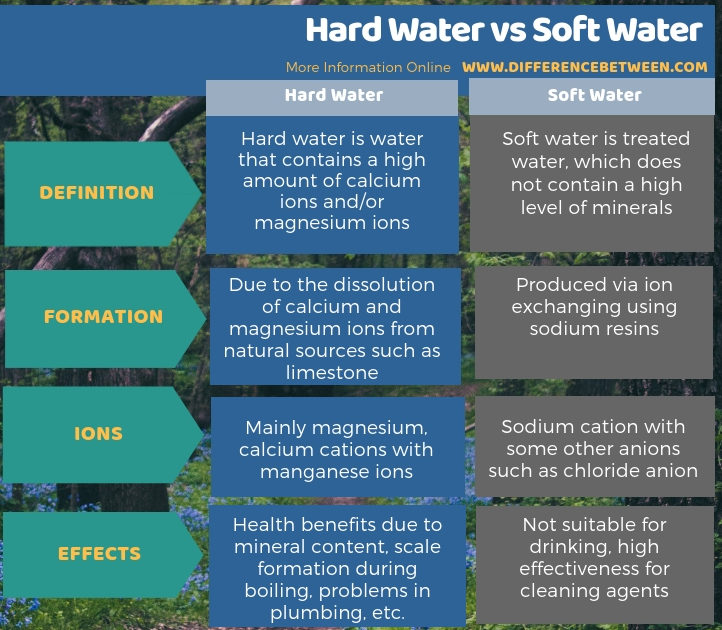
The key difference between hard water and soft water is that hard water contains lots of dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium whereas soft water has been treated, thus removing all minerals except sodium.
The difference between hard and soft water is in their composition. Hard water contains a lot of dissolved minerals (mainly calcium and magnesium) whereas the only ion present in soft water is sodium as it has been treated before being supplied to our homes. Rainwater, when it pours down, is soft; however, when it seeps under the ground, it picks up a lot of minerals such as chalk, calcium, magnesium, and lime.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Hard Water
3. What is Soft Water
4. Side by Side Comparison – Hard Water vs Soft Water in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Hard Water?
Hard water is water that contains a high amount of calcium ions and/or magnesium ions. Sometimes, there can be even manganese ions (Mn+2). When a waterway passes through calcium carbonates or magnesium carbonates such as chalk or limestone, it becomes hard water due to the dissolving of these substances, forming calcium and magnesium ions.
When concerning the effects of hard water, there are both positive and negative effects. For example, hard water has health benefits due to the presence of minerals – calcium and magnesium. As a negative effect, we can say that soap is less effective in cleaning when we use it with hard water.

Figure 1: Effects of Hard Water
The water hardness is of two types; temporary hardness and permanent hardness. Temporary hardness is a result of dissolved bicarbonate minerals such as calcium bicarbonate and magnesium bicarbonate. Permanent hardness comes from dissolved calcium sulfate and/or magnesium sulfates.
What is Soft Water?
Soft water is the treated water in which sodium is the only cation present. Therefore, soft water tastes salty and may not be suitable for drinking. It is because natural minerals dissolved in water gives us various health benefits, which soft water does not give.

Figure 2: Ion Exchange Resin Beads
However, people use soft water because hard water can cause problems in plumbing and lowers the effectiveness of cleaning agents. In order to soften hard water, we have to remove the minerals in hard water. For this purpose, we can use sodium resins as ion exchangers. However, sodium and some other anions will remain in the water while most cations are removed.
What is the Difference Between Hard Water and Soft Water?
Hard water and soft water are two types of water that have different mineral compositions. The key difference between hard water and soft water is that hard water contains lots of dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium whereas soft water is treated water, which does not contain a high level of minerals. Though hard water has health benefits due to mineral content, scale formation during boiling, problems in plumbing, etc are some negative aspects of it. On the other hand, while soft water is not suitable for drinking, it is highly effective for cleaning agents.
Below infographic provides more details on the difference between hard water and soft water.
Summary – Hard Water vs Soft Water
Hard water and soft water are two forms of water. The key difference between hard water and soft water is that hard water contains lots of dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium, but as soft water has been treated, all minerals except sodium has been removed.
Reference:
1. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. “What Hard Water Is and What It Does.” ThoughtCo, Jun. 22, 2018, Available here.
2. Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. “Chemistry of Hard and Soft Water.” ThoughtCo, Jan. 24, 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “hard water” By Graeme Maclean (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
2. “Ion exchange resin beads” By Bugman at English Wikipedia – Transferred from en.wikipedia to Commons by GcG. (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau260wKubZq%2BRqbKzecCnm2auo2LAsLLTZq6arJWnfA%3D%3D