The key difference between Glauber salt and common salt is that Glauber salt contains hydrated sodium sulfate, whereas common salt contains sodium chloride as the major component.
Both Glauber salt and common salt are inorganic compounds and are salts of sodium. Glauber salt contains the sulfate salt of sodium, while common salt contains the chloride salt of sodium.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Glauber Salt
3. What is Common Salt
4. Similarities Between Glauber Salt and Common Salt
5. Side by Side Comparison – Glauber Salt vs Common Salt in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Glauber Salt?
Glauber salt is the decahydrate form of sodium sulfate. This substance is also named mirabilite. The chemical formula of this compound is Na2SO4.10H2O. Decahydrate means the sodium sulfate molecule is associated with 10 water molecules. This material is a vitreous mineral and has a white or colourless appearance. This salt material is formed as an evaporite from brines containing sodium sulfate. Furthermore, Glauber salt occurs naturally in saline playa lakes and around saline springs. This material was named after the scientist Johann Rudolf Glauber.
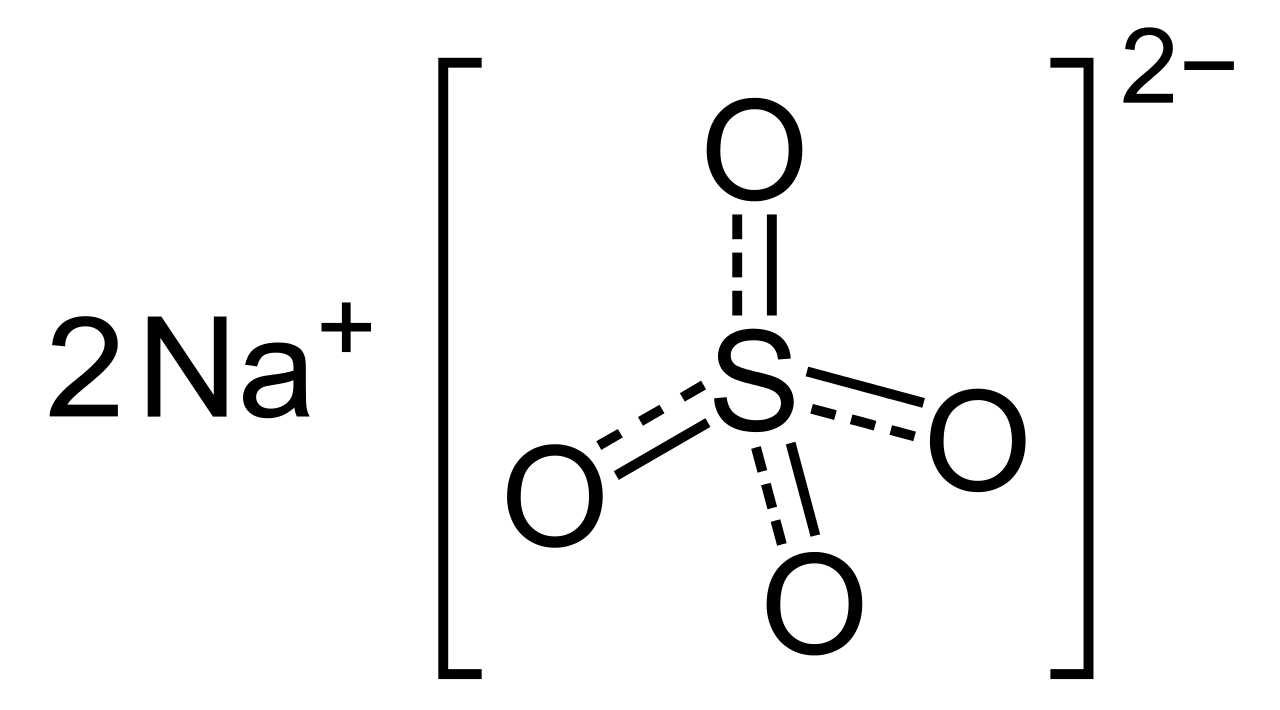
Figure 01: Chemical Structure of Sodium Sulfate
When considering the properties of Glauber salt, it is quite unstable in dry air. Therefore, when this salt is placed in dry air, we can observe the rapid dehydration of this salt. Upon this dehydration reaction, Glauber salt crystals tend to convert into a white powder, which is the anhydrous form of sodium sulfate. This resultant white powder is often named thenardite.
Glauber salt crystals crystallize in a monoclinic crystal shape. The texture of this substance can be granular, coarse or well-formed crystals. Apart from that, Glauber salt crystals are usually arranged in an octahedral crystal lattice structure.
What is Common Salt?
Common salt is table salt we use for household needs, and it mainly contains sodium chloride. Salt is a mineral that is mainly composed of sodium chloride. Therefore, the chemical formula for this compound is NaCl. This compound is present in vast quantities in seawater. For example, open ocean has 35 g/L solid sodium chloride. In general, this compound is essential for our consumption in day-to-day life. The major processes that form salt are mining salt mines and evaporation of seawater. The edible form of this compound is essential for human health and for most other animals as well.

Figure 02: Sea Salt Production from Brine
Moreover, salt is one of the five basic taste sensations. It is, therefore, the main ingredient in many foods. The widely available form is iodized salt which contains added potassium iodide. Most of the times, we add salt to food processing (as an ingredient in processed food) for both preservation and flavouring.
What are the Similarities Between Glauber Salt and Common Salt?
- Glauber salt and common salt are salts of sodium.
- Both are water-soluble compounds.
What is the Difference Between Glauber Salt and Common Salt?
Glauber salt and common salt are salt compounds of sodium. The key difference between Glauber salt and common salt is that Glauber salt contains hydrated sodium sulfate, whereas common salt contains sodium chloride as the major component. Moreover, Glauber salt has a bitter taste while common salt has a salty taste.
Below is a summary of the difference between Glauber salt and common salt in tabular form.

Summary – Glauber Salt vs Common Salt
Both Glauber salt and common salt are inorganic compounds, and they are salts of sodium. Glauber salt contains the sulfate salt of sodium, while common salt contains the chloride salt of sodium. The key difference between Glauber salt and common salt is that Glauber salt contains hydrated sodium sulfate, whereas common salt contains sodium chloride as the major component.
Reference:
1. What Is Glauber’s Salt? Key Properties and Uses (with FAQs). Byjus. 18 May 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Sodium sulfate” By Kemikungen – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Loading sea salt at evaporation pond, Walvis Bay (2014)” By Olga Ernst – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26zy5qsm52iYsCiuNNmmKecXZi8rrnOp2SsmZypfA%3D%3D