The key difference between fibronectin and laminin is that fibronectin is a glycoprotein that exists mainly in the extracellular matrix and blood plasma while laminin is a glycoprotein that exists mainly in the basal lamina.
Extracellular matrix, which is between tissues and organs surrounds the cells and provides structural and biochemical support to the cells. It consists of different extracellular components such as collagen, enzymes, and glycoproteins. Fibronectin and laminin are two important glycoproteins found in the extracellular matrix. Both are high molecular weight proteins combined with oligosaccharides. Also, fibronectin and laminin bind with different specific cell-surface cellular adhesion molecules in order to facilitate cell adhesion. Hence, these molecules are crucial in cell adhesion as well as in migration and differentiation.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Fibronectin
3. What is Laminin
4. Similarities Between Fibronectin and Laminin
5. Side by Side Comparison – Fibronectin vs Laminin in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Fibronectin?
Fibronectin is a high molecular weight glycoprotein present in the extracellular matrix. They bind with integrins, which are trans-membrane receptor proteins. Fibronectin binds mainly with collagen fibers in the extracellular matrix and helps in the cell movements through the matrix. Cells secrete these fibronectins.
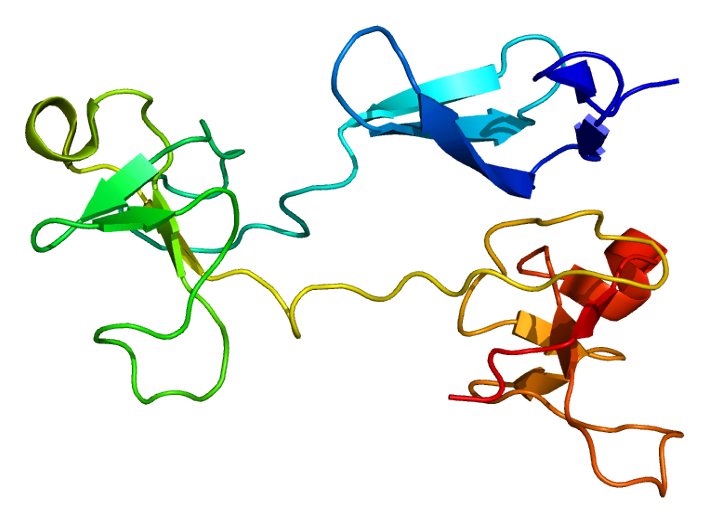
Figure 01: Fibronectin
In the beginning, fibronectin exists as an inactive form. Once they bind with integrins, they form dimmers and become functionally active. Apart from aiding the cell movements, fibronectins help in the formation of blood clots at the sites of injuries in order to prevent bleeding. Therefore, they are important in wound healing.
What is Laminin?
Laminin is also a glycoprotein present in the extracellular protein. However, laminin is mainly present in the basal lamina, which is a part of the extracellular matrix. Laminin is also a high molecular weight protein. It consists of three subunits: α, β, and γ chains. Moreover, Laminin is able to bind with other proteins present in the extracellular matrix, showing properties similar to fibronectin. Hence, it helps in reinforcing the extracellular matrix structure and assists cell adhesion.
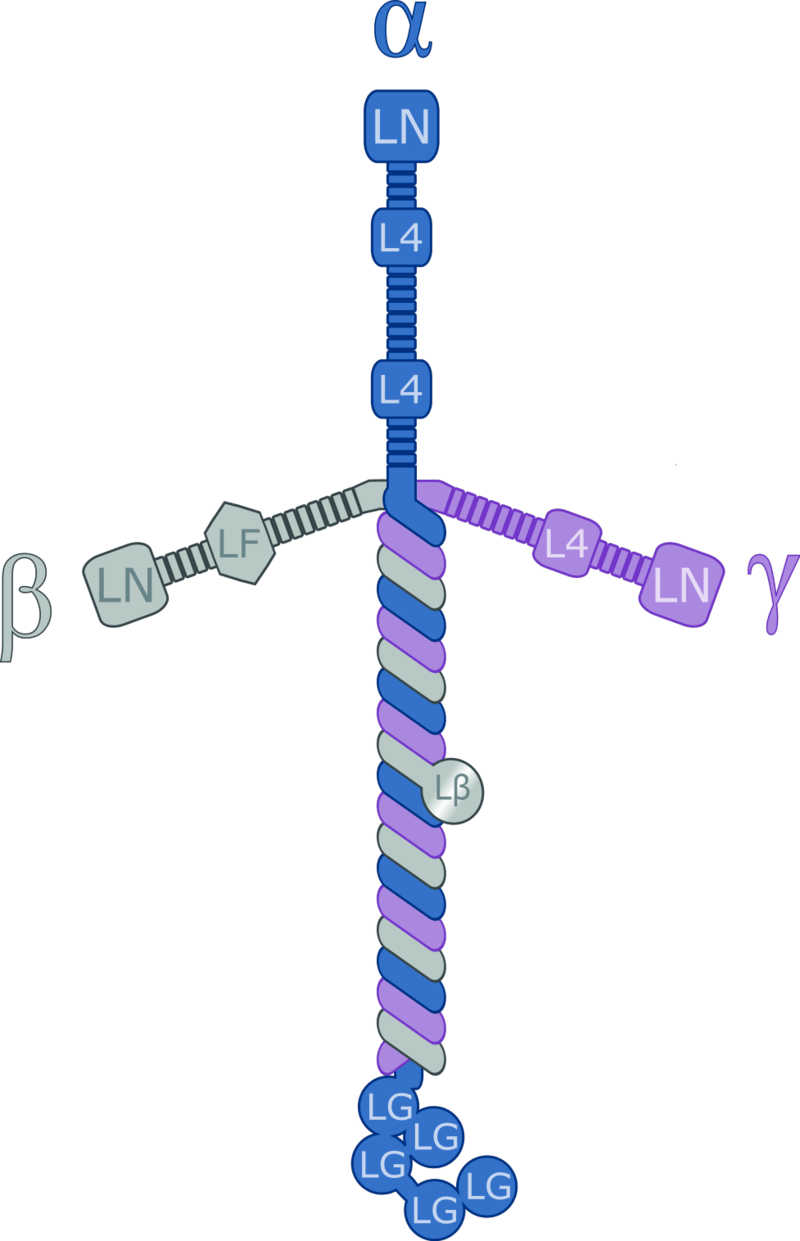
Figure 02: Laminin
Furthermore, laminin is a primary component of the lung basement membrane and provides structural support for the lung. Most importantly, laminin is essential for neural development and peripheral nerve repair.
What are the Similarities Between Fibronectin and Laminin?
- Fibronectin and laminin are two types of high-molecular-weight glycoproteins in the extracellular matrix.
- They are proteins.
- Also, both are crucial in cell adhesion, migration, growth, and differentiation.
- Moreover, both proteins are able to bind with other proteins present in the extracellular matrix.
- Furthermore, both molecules aid in reinforcing the extracellular matrix structure.
What is the Difference Between Fibronectin and Laminin?
Fibronectin is a glycoprotein found in the extracellular matrix while laminin is another glycoprotein mainly present in the basal lamina of the epithelia. So, this is the key difference between fibronectin and laminin. Furthermore, a structural difference between fibronectin and laminin is that the fibronectin is a homodimer while laminin is a heterodimer.
Moreover, fibronectin is a high molecular weight protein, which is about ~ 440 kDa in weight while the molecular weight of laminin is ~400 to ~900 kDa. Therefore, we can consider this also as a difference between fibronectin and laminin. Besides, fibronectin is important in wound healing while laminin is important in the development of neurons and peripheral nerve repair. Thus, this is the functional difference between fibronectin and laminin.
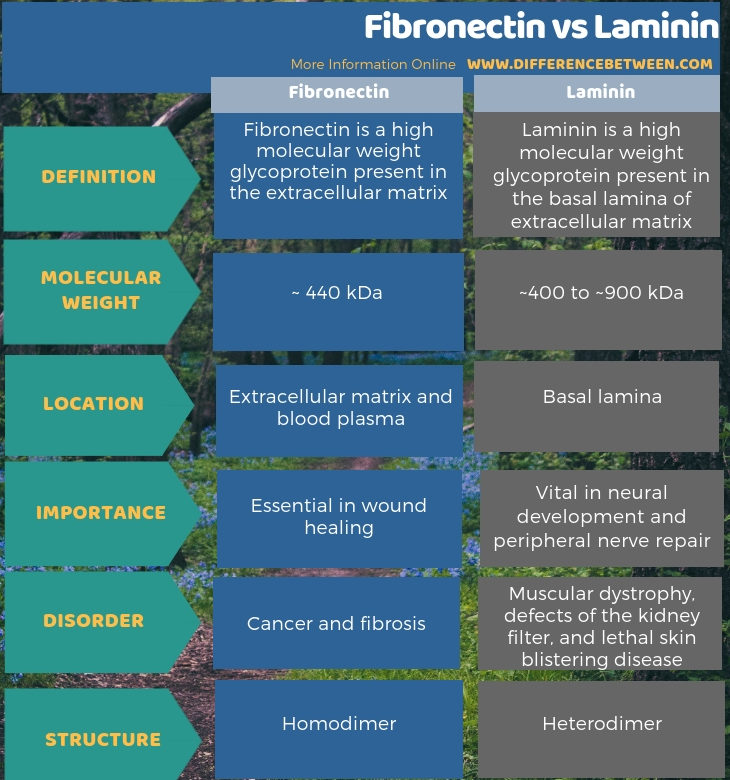
Summary – Fibronectin vs Laminin
Fibronectin and laminin are two glycoproteins present in the extracellular matrix. They are high molecular weight proteins that can bind with other proteins and aid in the cell adhesion and cell movements. Fibronectins are responsible for wound healing since they are involved in blood clotting. On the other hand, laminin is important for reinforcing the extracellular matrix structure, in neural development and peripheral nerve repair. In addition, fibronectin is a homodimer while laminin is a heterodimer. Thus, this summarizes the difference between fibronectin and laminin.
Reference:
1. “Laminin.” Laminin – an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics, Available here.
2. “Extracellular Matrix.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 15 Feb. 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Protein FN1 PDB 1e88” By Emw – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Laminin111” By Gad Armony – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26yyJupqKaVmMGquoyapZ1lnJa6qrrIp2Y%3D