The key difference between ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is that ethanol fermentation produces ethanol as a byproduct, whereas lactic acid fermentation produces lactate as a byproduct.
Fermentation is a process that takes place under anaerobic conditions. Therefore, it occurs in the absence of molecular oxygen. Many microbes, plants, and human muscle cells are capable of undergoing fermentation. During fermentation, sugar molecules are converted into alcohols and acids. This chemical reaction has great usage in the industrial production of dairy products, bakery products and alcoholic beverages.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Ethanol Fermentation
3. What is Lactic Acid Fermentation
4. Side by Side Comparison – Ethanol Fermentation vs Lactic Acid Fermentation in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Ethanol Fermentation?
Ethanol fermentation, also known as alcoholic fermentation, is a biological process in which a conversion of sugars into cellular energy occurs. The sugar molecules that can undergo this process include glucose, fructose, and sucrose. During the production of cellular energy, this process produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as well. These are the byproducts of ethanol fermentation.
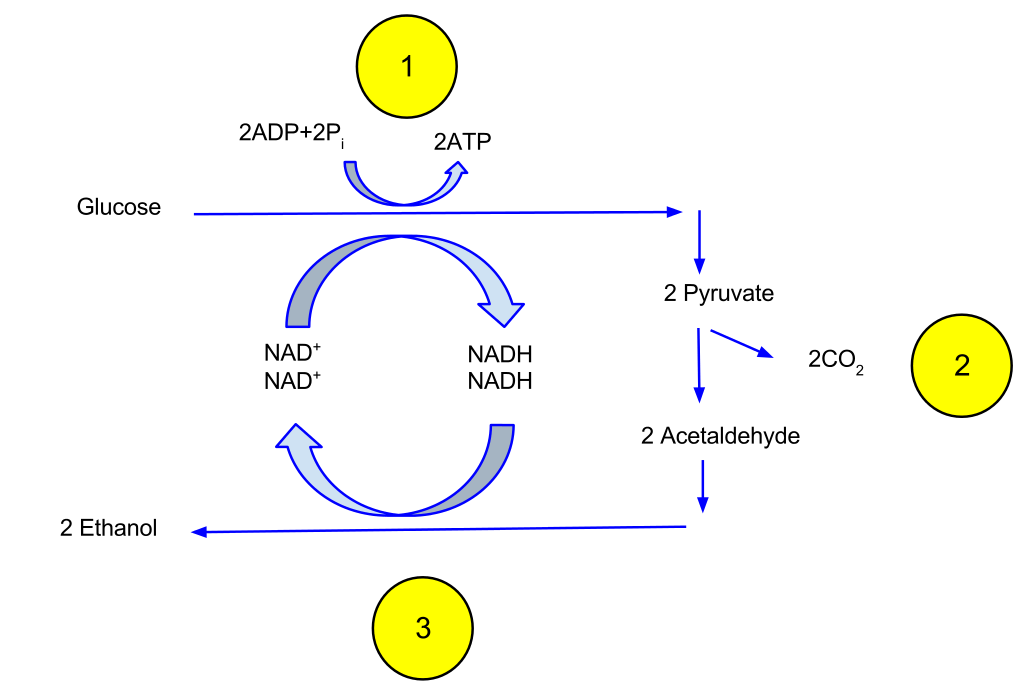
Figure 01: Ethanol Fermentation Process
This fermentation occurs in the presence of yeast and in the absence of oxygen gas. Therefore, we can name it an anaerobic biological process. Moreover, this process takes place in some fish species such as goldfish and provide these fish with energy when there is not enough oxygen.
Usually, ethanol fermentation converts one mole of glucose into two moles of ethanol and two moles of carbon dioxide. This produces two moles of ATP. When considering the sucrose molecule, it contains two sugar molecules: glucose and fructose linked to each other. Therefore, when sucrose is used for ethanol fermentation, the initial step is the cleavage of these molecules with the use of the invertase enzyme to break down the glycosidic bond between glucose and fructose. Thereafter, glucose is broken down into two pyruvate molecules through glycolysis, and then pyruvate is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide through two steps.
What is Lactic Acid Fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation is a biological process in which glucose or a similar sugar molecule is converted into cellular energy and metabolite lactate. Here, the sugar molecule can be either glucose or another six-carbon sugar molecule. Disaccharides such as sucrose can also be used. Lactate is lactic acid in solution. Lactic acid fermentation is an anaerobic process that takes place in some bacteria and animal cells, including muscle cells.
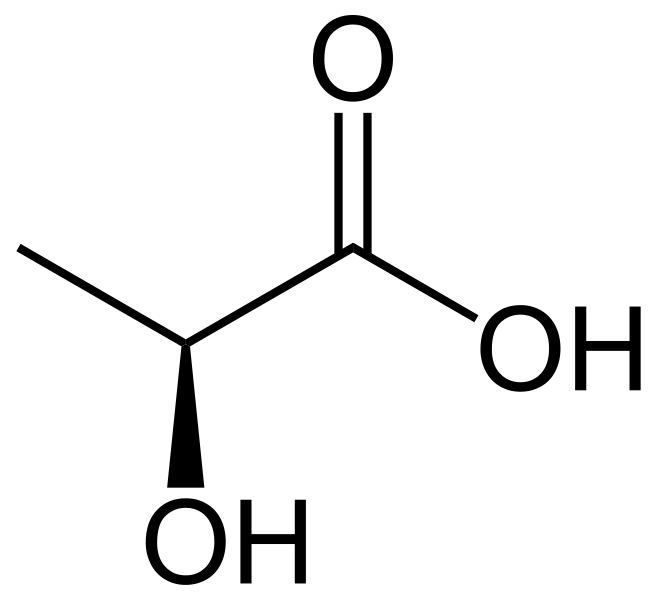
Figure 02: An Isomer of Lactic Acid
In the presence of oxygen in cells, the cell tends to bypass the fermentation process and perform cellular respiration. But there are some facultative anaerobic organisms that can perform both fermentation and respiration in the presence of oxygen gas.
There are three ways lactic acid fermentation can occur: homofermentative process, heterofermentative process, and bifidum pathway. In the homofermentative process, homofermentative bacteria can convert glucose into two molecules of lactate, and they can use this reaction to perform substrate-level phosphorylation in order to make two ATP molecules.
What is the Difference Between Ethanol Fermentation and Lactic Acid Fermentation?
Ethanol fermentation or alcoholic fermentation and is a biological process in which a conversion of sugars into cellular energy occurs. Meanwhile, lactic acid fermentation is a biological process in which glucose or a similar sugar molecule is converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate. The key difference between ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is that ethanol fermentation produces ethanol as a byproduct, whereas lactic acid fermentation produces lactate as a byproduct. Besides, ethanol fermentation has 29% efficiency whereas lactic acid fermentation has 41% efficiency.
The below infographic lists the differences between ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation in tabular form.

Summary – Ethanol Fermentation vs Lactic Acid Fermentation
Ethanol fermentation is a biological process in which a conversion of sugars into cellular energy occurs. Lactic acid fermentation is a biological process in which glucose or a similar sugar molecule is converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate. The key difference between ethanol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is that ethanol fermentation produces ethanol as a byproduct, whereas lactic acid fermentation produces lactate as a byproduct.
Reference:
1. “Lactic Acid Fermentation.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 2 Mar. 2021, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Ethanol fermentation-1” By Davidcarmack – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Lactic-acid-skeletal” By NEUROtiker – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26x06GYp6ecYrOmvsyepa2ZpJ68r3nAp5tmpJGYwaqvjJqaopxdm7KzucSnq5qsmaS7cA%3D%3D