The key difference between enthalpy and heat is that enthalpy is the amount of heat transferred during a chemical reaction at constant pressure whereas heat is a form of energy.
For study purposes in chemistry, we divide the universe into two: a system and surrounding. System is the subject of our investigation while the rest is the surrounding. Heat and enthalpy are two terms describing the energy flow and properties of a system.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Enthalpy
3. What is Heat
4. Side by Side Comparison – Enthalpy vs Heat in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Enthalpy?
In thermodynamics, the total energy of a system is the internal energy. Internal energy specifies the total kinetic and potential energy of molecules in the system. Internal energy of a system can be changed either by doing work on the system, or heating it. However, the change in internal energy is not equal to the energy that transfers as heat when the system is capable of changing its volume.
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic property and we can denote it by H. The mathematical relationship for this term is as follows:
H = U + PV
Here, H is enthalpy and U is the internal energy, P is the pressure and V is the volume of the system. This equation shows that the energy supplied as heat at a constant pressure is equal to the change in enthalpy. The term pV accounts for the energy required by the system to change volume against the constant pressure. Therefore, enthalpy is basically the heat of a reaction at constant pressure.
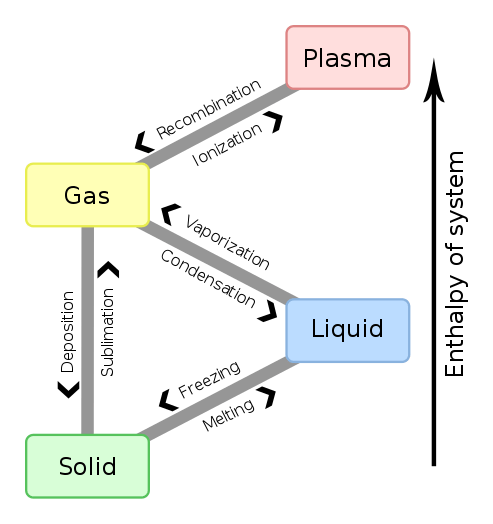
Figure 01: Enthalpy Changes for Phase Changes of Matter
Moreover, the enthalpy change (∆H) for a reaction in a given temperature and pressure is obtained by subtracting the enthalpy of reactants from the enthalpy of products. If this value is negative, then the reaction is exothermic. If the value is positive, then the reaction is said to be endothermic. The change in enthalpy between any pair of reactants and products is independent of the path between them. Moreover, enthalpy change depends on the phase of the reactants. For example, when oxygen and hydrogen gases react to produce water vapor, the enthalpy change is -483.7 kJ. But, when the same reactants react to produce liquid water, the enthalpy change is -571.5 kJ.
What is Heat?
The capacity of a system to do work is the energy of that system. We can do work on the system or the system can do work, which leads to increase or decrease the energy of the system accordingly. Energy of a system can be changed, not only by the work itself, by other means too. When the energy of a system changes as a result of temperature difference between the system and its surroundings, we refer to that energy transferred as heat (q); that is, energy has been transferred as heat.

Heat transfer takes place from high temperature to low temperature, which is according to a temperature gradient. Moreover, this process continues until the temperature between the system and the surrounding reach the same level. There are two types of heat transferring processes. They are endothermic processes and exothermic processes. Endothermic process is a process in which energy enters the system from the surroundings as heat while an exothermic process is one where heat is transferred from the system to the surroundings as heat.
What is the Difference Between Enthalpy and Heat?
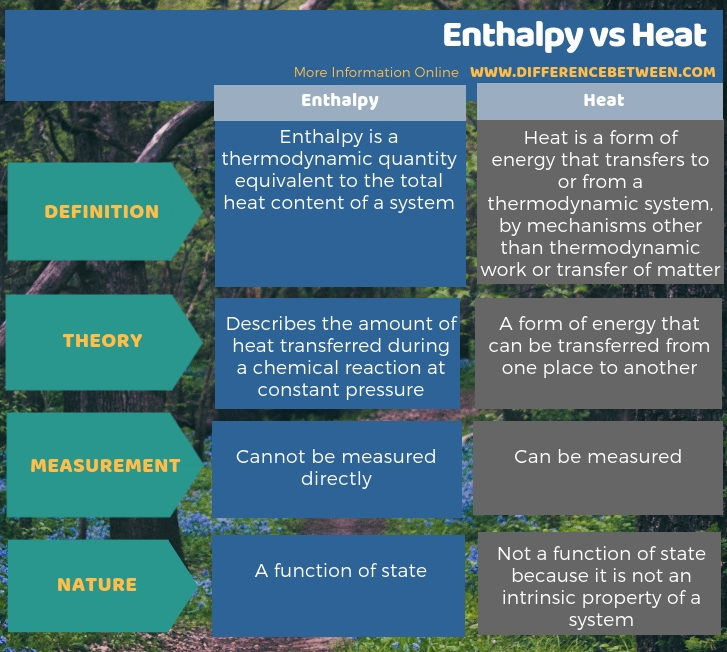
Most of the times, we use the terms enthalpy and heat interchangeably, but there is a slight difference between enthplay and heat. The key difference between enthalpy and heat is that enthalpy describes the amount of heat transferred during a chemical reaction at constant pressure whereas heat is a form of energy. Furthermore, enthalpy is a function of the state, whereas heat isn’t since heat is not an intrinsic property of a system. In addition, we cannot measure enthalpy directly, so we have to calculate it through equations; however, we can measure heat directly as a temperature change.
Summary – Enthalpy vs Heat
We often use the terms enthalpy and heat interchangeably, but there is a slight difference enthalpy and heat is that enthalpy describes amount of heat transferred during a chemical reaction at constant pressure whereas heat is a form of energy.
Reference:
1. Helmenstine, Anne Marie. “Enthalpy Definition in Chemistry and Physics.” ThoughtCo, Aug. 22, 2019, Available here
Image Courtesy:
1. “Phase change – en.” By F l a n k e r, penubag – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Fire Flare-Up Heat Free Picture” (CC0) via Needpix.com
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26xza2fmqSgrnqiusNmraxlmJqutXs%3D