The key difference between dikaryotic and diploid is that dikaryotic cell is the cell that contains two genetically distinct nuclei while diploid cell is a cell that contains two sets of chromosomes.
Generally, a cell contains only one nucleus. However, in some instances, cells contain more than one nucleus. In sexual reproduction, we can also observe cells with two nuclei. Dikaryon or dikaryotic cell is a cell at the stage of having two nuclei, especially seen in fungi. However, it is the moment which is prior to the karyogamy or nuclear fusion. When the karyogamy occurs, dikaryon transforms into a diploid cell, which is a cell that contains two sets of chromosomes.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Dikaryotic
3. What is Diploid
4. Similarities Between Dikaryotic and Diploid
5. Side by Side Comparison – Dikaryotic vs Diploid in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Dikaryotic?
Dikaryon is a cell that contains exactly two genetically distinct nuclei. This is a unique feature of fungi. Dikaryon is a result of plasmogamy. The fusion of male and female gametes occurs in sexual reproduction in order to produce a diploid zygote. It is known as fertilization or syngamy. Prior to haploid nuclei fusion, cell membranes of the two gametes fuse and then the two cytoplasms fuse with each other. The nuclei fusion delays for a certain time period. This process is known as plasmogamy.
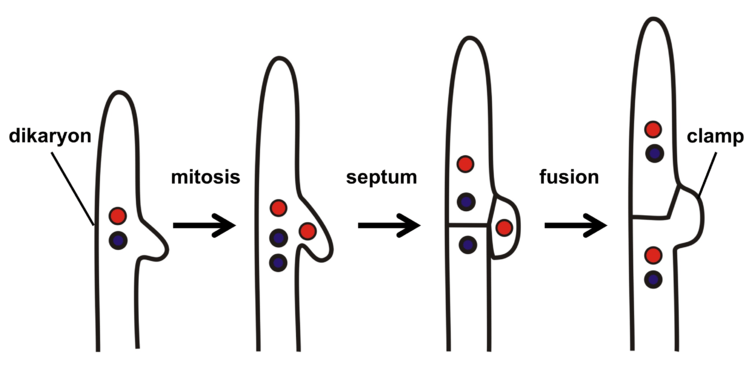
Figure 01: Dikaryotic Cell
Plasmogamy is feasible among two gametes or between two vegetative cells of fungi which play the role of gametes. In fact, it is one stage of sexual reproduction in fungi and it brings two nuclei close to each other for fusion. Plasmogay creates a new cell stage which differs from normal haploid or diploid cell as it has both male and female nuclei coexisting within the same cytoplasm without merging as n+n state. At this phase, the resulting cell is called a dikaryon or dikaryotic cell. Dikaryotic cell harbours a couple of nuclei from two mating types.
What is Diploid?
A diploid cell is a cell that contains two sets of chromosomes. Generally, a diploid cell receives one set of chromosomes from the mother while the other set of chromosomes from father. Therefore, a diploid cell contains maternal as well as paternal chromosomes. Somatic cells are normally diploid in nature. These cells divide by mitosis and produce diploid cells that are genetically identical. Gametes or haploid cells fuse during sexual reproduction and produce a diploid zygote, which is the basic cell for many organisms. A diploid cell is also known as a 2n cell.
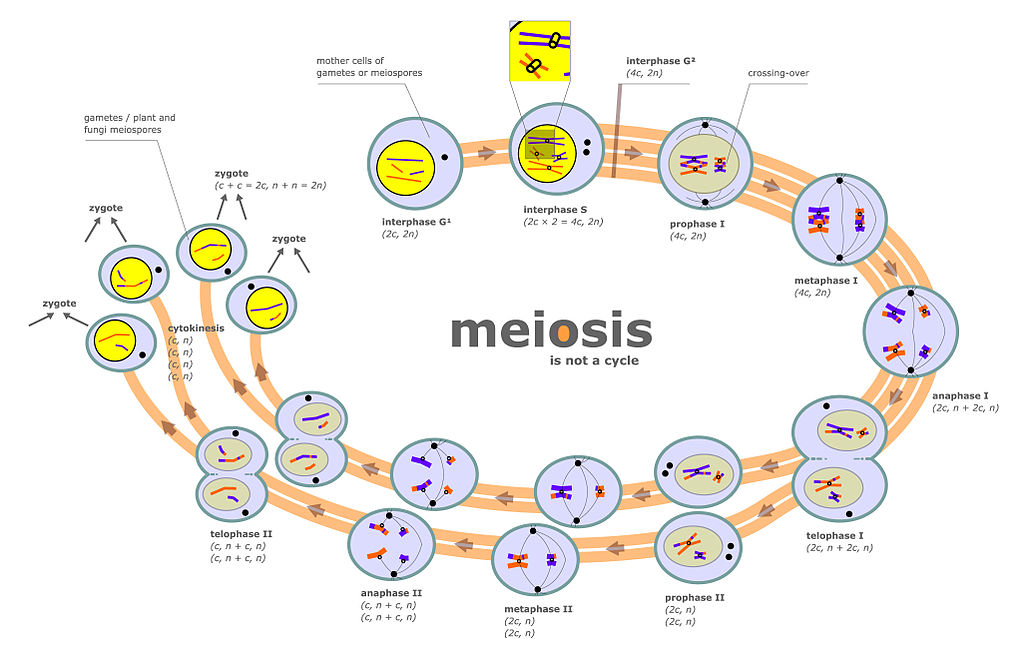
Figure 02: Diploid Cell Formation
Diploid cells are important in regeneration and cell or tissue repairing processes. By dividing via mitosis, diploid cell adds new cells in order to replace and repair tissues.
What are the Similarities Between Dikaryotic and Diploid?
- Dikaryotic and diploid cells are eukaryotic cells.
- They contain nuclei.
- Both are important in sexual reproduction.
What is the Difference Between Dikaryotic and Diploid?
A dikaryotic cell contains two genetically distinct nuclei. Meanwhile, a diploid cell contains two sets of chromosomes. Therefore, this is the key difference between dikaryotic and diploid.
Moreover, we can refer a dikaryotic cell as n+n cell, while a diploid cell as 2n cell. So, this is another difference between dikaryotic and diploid. Besides, a dikaryotic cell has two separate nuclei while a diploid cell has only one nucleus.

Summary – Dikaryotic vs Diploid
Dikaryotic and diploid cell are two types of eukaryotic cells. A dikaryotic cell is a unique feature of fungi. It is a cell containing two genetically distinct nuclei. Plasmogamy creates a dikaryotic cell during the sexual reproduction of fungi. On the other hand, a diploid cell is a normal cell that contains two sets of chromosomes. Moreover, a dikaryotic cell is in the state of n+n, while a diploid cell is in the state of 2n. So, this summarizes the difference between dikaryotic and diploid.
Reference:
1. “Dikaryon.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 27 Nov. 2019, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “03 01 02 development of clamp connection (M. Piepenbring)” By M. Piepenbring – M. Piepenbring (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Meiosis diagram” By Marek Kultys – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26wyKSYq7GfqbakecCnm2acmaW5sLXDaA%3D%3D