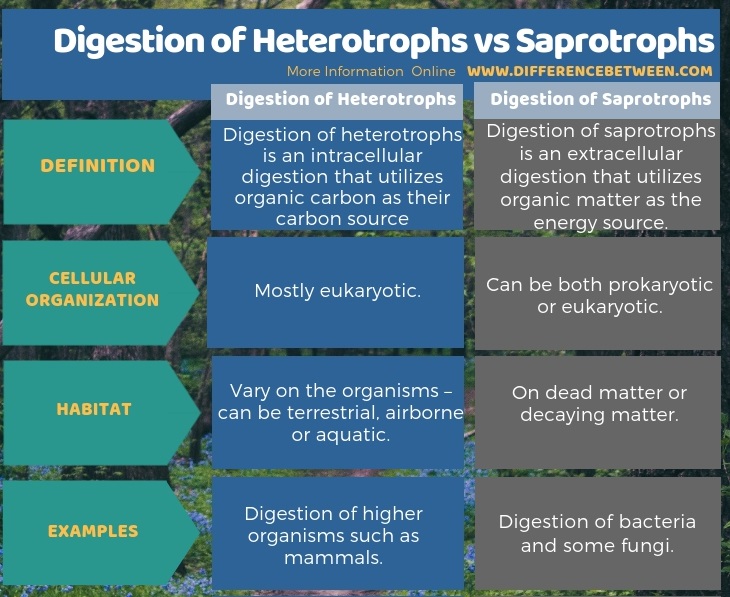
The key difference between digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs is that the digestion of heterotrophs is intracellular while the digestion of saprotrophs is extracellular.
Digestion is an important process for the survival of organisms. Through this process, nutrients become available for absorption by the organisms. Heterotrophic digestion is the process of intracellular digestion in organisms, which depend on organic food. Saprotrophic digestion is the process of extracellular digestion where the organisms depend on dead organic matter. Both digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs is important for the survival of the biosphere. Heterotrophs depend on organic matter from plants and other animal sources. On the other hand, saprotrophs directly depend on dead organic matter for their nutrition. Therefore, learning these digestion patterns help in studying nutritional relationships in organisms.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Digestion of Heterotrophs
3. What is Digestion of Saprotrophs
4. Similarities Between Digestion of Heterotrophs and Saprotrophs
5. Side by Side Comparison – Digestion of Heterotrophs vs Saprotrophs in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Digestion of Heterotrophs?
Heterotrophs are organisms which depend on organic carbon sources as its carbon source and depend on plants and other organisms for their survival. Heterotrophs can be herbivorous, carnivorous or omnivorous. Thus, digestion of heterotrophs takes place as intracellular (inside the cells or body) with the action of enzymes.
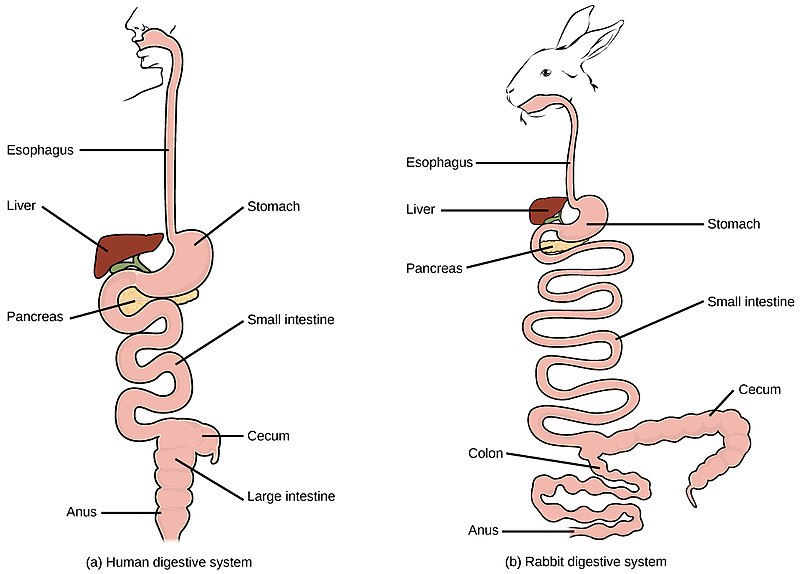
Figure 01: Digestion of Heterotrophs
The digestion of heterotrophs involves five steps. Those are ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion. They fist ingest the food from the external environment. The ingested food then undergoes digestion. Digestion can take place either mechanically with the help of the tongue and the teeth or chemically. Chemical digestion in heterotrophs facilitates by the enzymes and hormones that act on food. The digested food is then absorbed and assimilates thus enabling it to be used by the organism. Finally, the undigested food egests as faeces. Thus, heterotrophs convert complex food into simple food intracellularly. This enables them to obtain energy as these simple monomers act as energy sources to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What is Digestion of Saprotrophs?
Saprotrophs are organisms which solely depend on the dead organic matter as their nutrition source. They live on decaying matter, wood or on dead leaves. They are found mostly in the soil layers. Saprotrophs can be prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea or eukaryotes such as fungi.
Saprotrophs do not have the ability to take in complex foods. Therefore, they secrete digestive enzymes to the external environment that converts the complex organic matter to simple monomers. Upon digestion of the complex matter, the saprotrophs then absorb the simple matter. Hence, saprotrophs perform extracellular digestion.

Figure 02: Digestion of Saprotrophs
Saprotrophs can also be herbivorous depending on dead leaves and wood matter or omnivorous that depend both on dead animal and plant matter. They are very important decomposers that aid in the cleaning of the dead matter in the environment.
What are the Similarities Between Digestion of Heterotrophs and Saprotrophs?
- Both these organisms can be herbivorous or omnivorous.
- Both the digestion of Heterotrophs and Saprotrophs produce digestive enzymes.
- Digestion of Heterotrophs and Saprotrophs are mostly aerobic in nature.
- They convert complex matter to simple matter before absorption.
- They both use organic carbon sources as nutritional sources.
What is the Difference Between Digestion of Heterotrophs and Saprotrophs?
Digestion can be intracellular or extracellular. Heterotrophs have intracellular digestion while saprotrophs have extracellular digestion. This is the key difference between digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs. Another difference between digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs arising from the above is that the heterotrophs and saprotrophs secrete digestive enzymes. However, heterotrophs release them inside the body while saprotrophs release enzymes to the external environment on the dead organic matter. Mammals mainly humans have intracellular digestion whereas, fungi and bacteria have extracellular digestion.
The below infographic tabulates the difference between digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs.
Summary – Digestion of Heterotrophs vs Saprotrophs
Both heterotrophs and saprotrophs depend on organic matter as their modes of nutrition. The digestion of heterotrophs is intracellular digestion, which happens after ingesting the complex food forms. In contrast, Saprotrophs release digestive enzymes on the dead matter that convert the complex organic matter to simple organic matter and then absorb the digested organic matter. Thus, the digestion of Saprotrophs is extracellular digestion. This is the difference between digestion of heterotrophs and saprotrophs.
Reference:
1.“Heterotrophic Nutrition.” Confidentiality. Available here
2.Wilson, Andrew W. “Saprotroph.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 24 May 2018. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Figure 34 01 05ab”By CNX OpenStax , (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”Mycena interrupta”By JJ Harrison – Own work, (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26wyKCcrKyZpLtuu8Vmn56slae8tb7OqZ%2BsZZGjsW6%2FwKmpqKyipL2pv44%3D