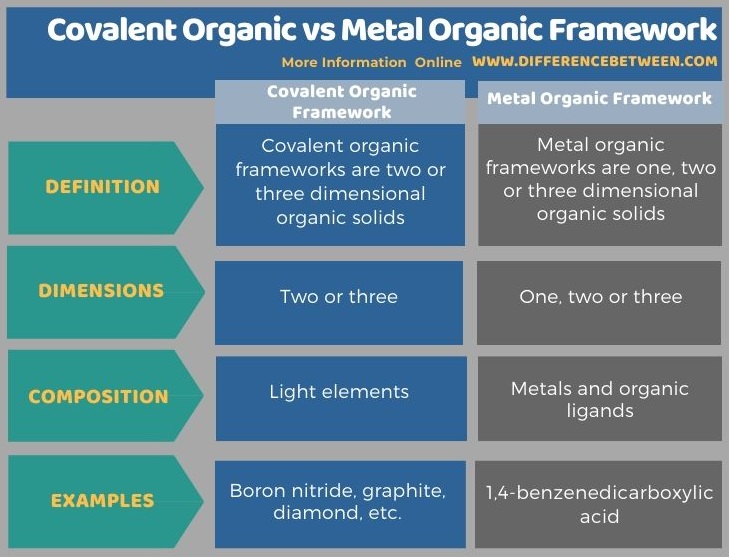
The key difference between covalent organic and metal organic framework is that covalent organic frameworks are structures having covalent bonds whereas metal organic frameworks are structures having coordination bonds.
Covalent and metal organic frameworks are classes of compounds having unique properties. Both of these classes contain materials that are recognized as organic solid compounds. Generally, covalent organic frameworks are compounds having two or three-dimensional properties while metal organic frameworks are compounds having one, two or three-dimensional properties.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is a Covalent Organic Framework
3. What is a Metal Organic Framework
4. Side by Side Comparison – Covalent Organic vs Metal Organic Framework in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is a Covalent Organic Framework?
Covalent organic frameworks are two or three dimensional organic solids. We can abbreviate them as COFs. These material have extended structures with building blocks which are bonded to each other via covalent chemical bonds. These linkages are strong covalent bonds. Usually, COFs are porous and crystalline structures. Moreover, these materials are made of light elements; mainly hydrogen (H), boron (B), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O). These light chemical elements usually form strong covalent bonds. Some common examples of covalent organic framework include diamond, graphite, and boron nitride.

Figure 01: Covalent Organic Framework
When considering the structure of a covalent organic framework, these materials are porous structures with crystalline nature and contains secondary building blocks. These building blocks assemble to form a periodic structure. The combination of these building blocks can lead to forming an infinite number of organic frameworks.
There are different uses of covalent organic frameworks including hydrogen storage, methane storage, harvesting a wide range of wavelengths and photons from light, allowing the migration of energy, carbon capturing, electrocatalysis, etc.
Metal-organic frameworks are one, two or three-dimensional organic solids. It is a class of compounds containing solids composed of metal ions or clusters that are coordinated to organic ligands. This is a subclass of coordination polymer materials. The specific feature of this material class is its porous structure. The organic ligands in these structures are sometimes called “struts”.
Formally, a metal organic framework is a coordination complex with organic ligands having potential voids. This coordination network extends through repeating coordination entities in one dimension and there are crosslinks between two or more individual chains which make the two or three-dimensional structure.

Figure 02: Metal Organic Framework
Sometimes, the pores stay stable during the elimination of guest molecules such as solvents and these pores can also be refilled with other compounds. This property makes these metal organic frameworks better storage places for gases and, these materials are also important in gas purification, gas separation, catalysis, as conducting solids, and as supercapacitors.
The key difference between covalent organic and metal organic framework is that the covalent organic frameworks are structures having covalent bonds whereas metal organic frameworks are structures having coordination bonds. Besides, generally, covalent organic frameworks are compounds having two or three-dimensional properties while metal organic frameworks are compounds having one, two or three-dimensional properties.
Moreover, boron nitride, graphite, diamond, etc. are examples of covalent organic frameworks while 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid is an example of metal organic frameworks.
Below infographic summarizes the difference between covalent organic and metal organic framework.
Summary – Covalent Organic vs Metal Organic Framework
Covalent and metal organic frameworks are classes of compounds having unique properties. The key difference between covalent organic and metal organic framework is that the covalent organic frameworks are structures having covalent bonds whereas metal organic frameworks are structures having coordination bonds.
Reference:
1. “Covalent Organic Framework.” Science Direct. Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Covalent Organic Frameworks (space-filling diagram)” (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Metal-Organic Framework (6898958430)” By National Institute of Standards and Technology – Metal-Organic Framework (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vzq%2BYpZ2eqXqwvsaapaKbXZa7pXnMnquapF2kv6itzaKaZp6ilrqmw86romg%3D