Key Difference – Cell Organelles vs Cell Inclusions
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms. It is the basic building block of life that has the self-replicating ability. The cell was first discovered by an English Scientist Robert Hooke in 1665. The cell theory was proposed in 1839 for the first time by Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. The organisms can be classified based on the number of cells; unicellular or multicellular. Bacteria are unicellular organisms. On the other hand, fungi, plants and animals are multicellular organisms. The cell has a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane known as plasma membrane. It also contains cell organelles such as Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, microtubules, filaments, chloroplast etc. and cell inclusions such as pigment granules, fat droplets, secretory products, glycogen, lipids and crystalline inclusions. The key difference between Cell Organelles and Cell Inclusions is that the cell organelles are living components and subcomponents of the cell that perform specific functions and act as cellular machines whereas cell inclusions are non living chemical compounds and by-products of cellular metabolism that are present in the cytoplasm. The cell inclusions contain reserved materials which are necessary for future use of the cells.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Cell Organelles
3. What are Cell Inclusions
4. Similarities Between Cell Organelles and Cell Inclusions
5. Side by Side Comparison – Cell Organelles vs Cell Inclusions in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Cell Organelles?
The cell organelles can be defined as the membrane-bound internal structures that perform specific functions in the cell. They are also known as internal machines which are highly important for cellular activities. They are mini-organs that have single or double layered phospholipid membrane. There is a number of cell organelles present in the cell as indicated below.
Cell organelles Function
Nucleus It stores genetic material (DNA or RNA) of the cell.
Mitochondrion It involves in energy production.
Golgi apparatus It involves in protein modification and export.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) It involves in lipid production, protein production, and detoxification.
Lysosomes It contains various hydrolytic enzymes (recycling and security).
Chloroplast It involves in photosynthesis (glucose production).
Cytoskeleton It provides cell stability and helps in movement.
Microtubules It helps in cell movement.
Intermediate Filaments It provides structural stability to the nuclear envelope.
Microfilaments It helps in cell movement.
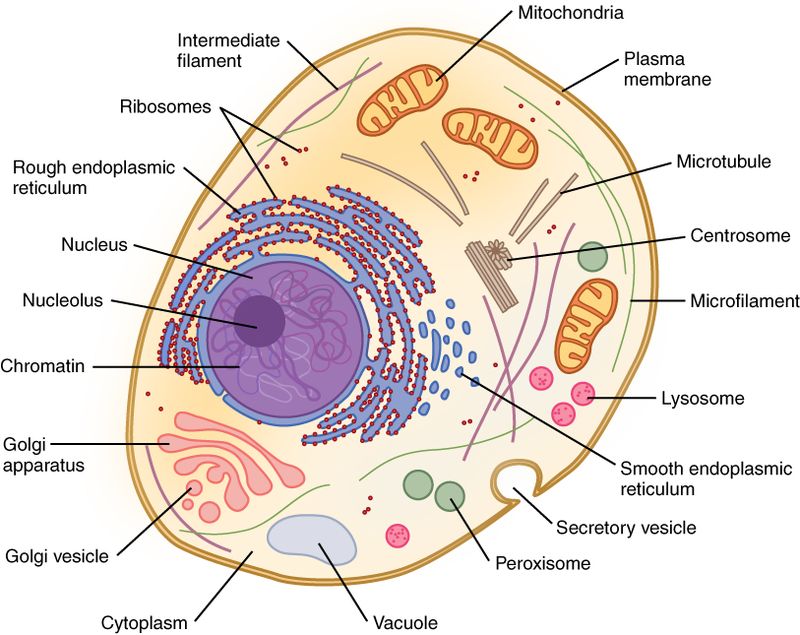
Figure 01: The Cell Organelles
It is highly important to know that membrane-bound organelles are only found in the eukaryotic organisms. They are absent in the prokaryotic organisms like bacteria and archaea.
What are Cell Inclusions?
The cell inclusions or cytoplasmic inclusions can be defined as non-living substances that are not able to carry out any metabolic activity. And they are not bound by any membrane. These inclusions include; stored nutrients, secretory products and pigment granules etc. They are present in both prokaryotic cells as well as in eukaryotic cells.
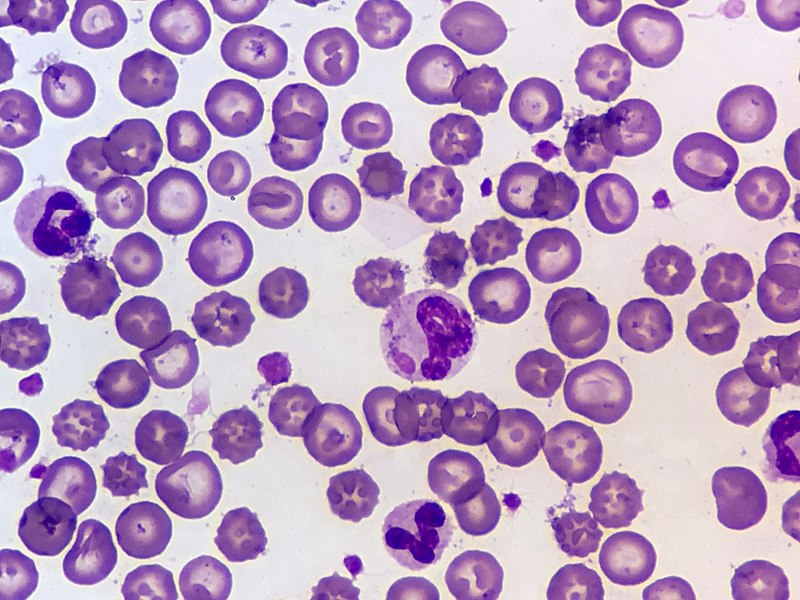
Figure 02: Cell Inclusions
Examples of Cell Inclusions include,
- Glycogen granules in liver muscle cells,
- Lipid droplets in fat cells (lipids in adipocytes and hepatocytes),
- Pigment granules of skin and hair cells (melanin in melanocytes),
- Water containing vacuoles,
- Crystals of various types of cells in human testis (Sertoli cells and Leydig cells),
- Secretory products such as hormones, mucus, digestive enzymes, neurotransmitters etc.
They are normally termed as reserved materials or cellular fuels. The bacteria are having cell inclusions such as polyphosphates, poly-beta-hydroxy-butyrate, glycogen, gas vacuoles, sulfer globules, ribosomes and carboxysomes.
What are the Similarities Between Cell Organelles and Cell Inclusions?
- Both are present in the interior of the cell.
- Both are important for living cell on various occasions.
- Both are present in the cytoplasm.
- The cell membrane is known as “plasma membrane” protects both of them.
What is the Difference Between Cell Organelles and Cell Inclusions?
Cell Organelles vs Cell Inclusions | |
| Cell organelles are the membrane-bound internal structures that perform specific functions in the cell. | Cell inclusions are the non-living substances that are not able to carry out any metabolic activity. |
| Function | |
| The cell organelles perform specific functions in the cell. | The cell inclusions do not carry out any specific metabolic functions. |
| Presence in Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells | |
| The cell organelles are present only in the Eukaryotic organisms’ cells. | The cell inclusions are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. |
| As Cellular Machine and Fuel | |
| The cell organelles are described as cellular machines. | The cell inclusions are described as cellular fuels. |
| Living or Non Living Structures | |
| The cell organelles are known as living structures. | The cell inclusions are known as non-living structures. |
| Activity | |
| The cell organelles perform metabolic activities. | The cell inclusions are used for storage, as excretory and secretory materials. |
| Growth Capability | |
| The cell organelles are capable of growth. | The cell inclusions are not capable of growth. |
| Exporting Nature | |
| The cell organelles are always inside the cell and not exported out of the cell. | The cell inclusions may be exported out of the cell. |
Summary – Cell Organelles vs Cell Inclusions
The cell is the basic unit of living organisms. It is composed of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane called as plasma membrane. It also contains cell organelles such as; Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, peroxisomes, microtubules, filaments, chloroplast. And also cell contains cell inclusions such as pigment granules, fat droplets, secretory products, glycogen, lipids and crystalline inclusions. The cell organelles perform specific metabolic functions in the cell. On the other hand, the cell inclusions are not able to carry out any metabolic activity but help in cell organelles. Cell organelles are the cellular machines of the cell while cell inclusions play a role in fueling the cell organelles with different compounds and chemicals. This is the difference between cell organelles and cell inclusions.
Download the PDF Version of Cell Organelles vs Cell Inclusions
You can download PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation note. Please download PDF version here Difference Between Cell Organelles and Cell Inclusions
Reference:
1.Benditt, MD Earl P. “The Cell: Its Organelles and Inclusions.” JAMA, American Medical Association, 3 Oct. 1966. Available here
2.“Cell (Biology).” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 25 Dec. 2017. Available here
3.“Cytoplasmic inclusion.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 19 Nov. 2017. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.’0312 Animal Cell and Components’By OpenStax, (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=30131195
2.’Canine Distemper Virus Cytoplasmic Inclusion Body (Blood smear, Wright’s stain)’By Lance Wheeler – Own work, (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vxKWjZqeinK6vsculnKxlkaOxbsLSZpqepJxitq%2Bvy66qoqeeqHw%3D