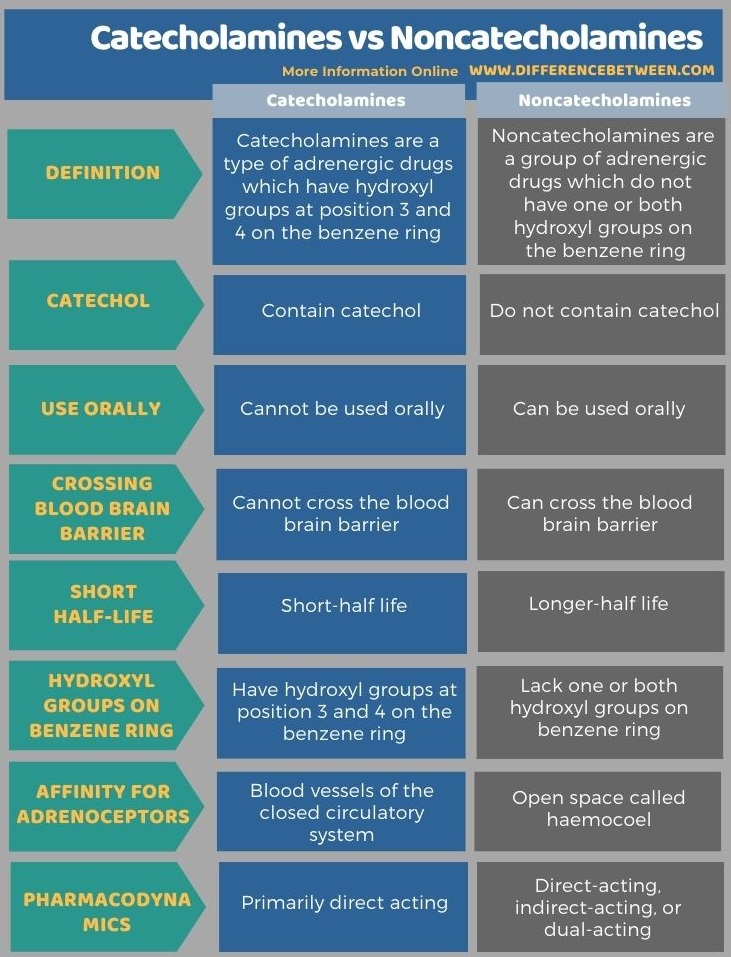
The key difference between catecholamines and noncatecholamines is that catecholamines are mainly direct-acting adrenergic drugs that have catechol, while noncatecholamine can be direct-acting, indirect-acting, or dual-acting adrenergic drugs that do not have catechol.
Adrenergic drugs mimic the effects of adrenergic nerve stimulation. Catecholamines and noncatecholamines are two types of adrenergic drugs. They can be direct-acting or indirect-acting. Indirect acting drugs do not bind to receptors, but direct-acting receptors bind to receptors. Moreover, direct-acting drugs are specific, while indirect-acting drugs are non-specific. Catecholamines show varying agonistic actions on the adrenoceptors. They are primarily direct-acting. Noncatecholamines can be direct-acting, indirect-acting, or dual-acting.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Catecholamines
3. What are Noncatecholamines
4. Similarities Between Catecholamines and Noncatecholamines
5. Side by Side Comparison – Catecholamines vs Noncatecholamines in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What are Catecholamines?
Catecholamines are various amines that function as hormones or neurotransmitters or both. Structurally, 3, 4, dihydroxybenzenes are called catechol. Therefore, the drugs which have this structure are called catecholamines. Adrenergic neurons release synaptic vesicles which contain catecholamines. Catecholamine synthesis needs the precursor called tyrosine. There are endogenous catecholamines that are naturally occurring in the body. Epinephrine, norepinephrine and dopamine are some of the natural catecholamines. There are synthetic catecholamines as well. Isoproterenol, dobutamine and rimiterol are several synthetic catecholamines. All catecholamines are potentially arrhythmogenic. Some cause hypertension. Moreover, some cause central nervous system effects such as fear, anxiety and restlessness.
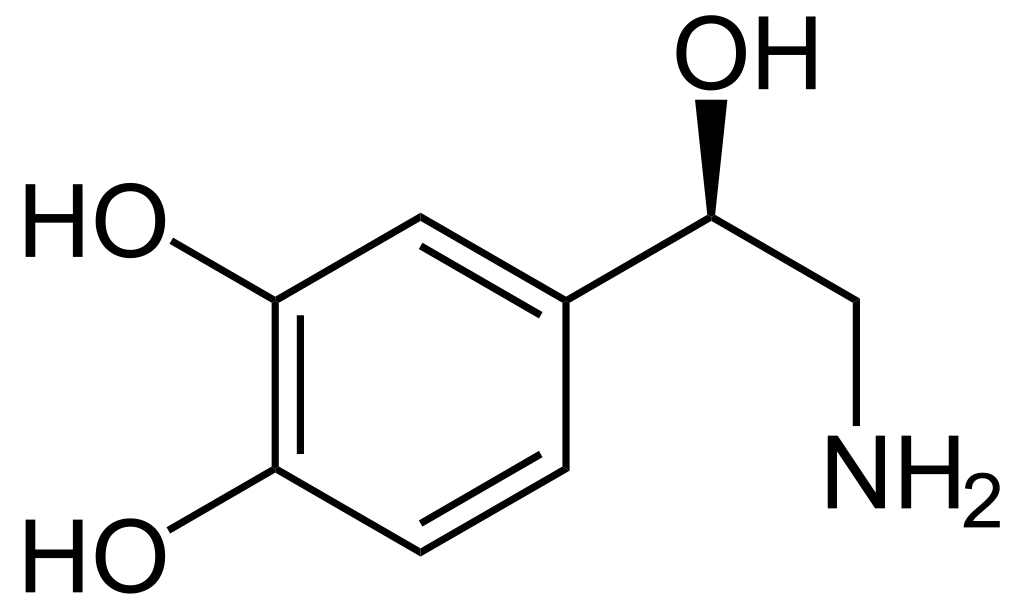
Figure 01: Catecholamine
Catecholamines are a type of adrenergic drugs. They are not effective by the oral route. Hence, they are usually given parenterally. Catecholamines have short half-life due to their rapid metabolism. They show direct action and have a high affinity for adrenoceptors. Catecholamines cannot cross the blood brain barrier. Therefore, they have minimal effect on CNS.
What are Noncatecholamines?
Noncatecholamines are the second group of adrenergic drugs. Noncatecholamines do not have hydroxyl groups on the benzene ring. Most noncatecholamines are effective orally. They have moderate to a poor affinity for adrenoceptors. Most importantly, noncatecholamines degrade slowly. Hence, they have a moderate to longer half-life. Moreover, noncatecholamines can cross the blood-brain barrier and are found in high concentrations in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Thus, they can produce a significant effect on CNS. Noncatecholamines can be direct-acting, indirect-acting, or dual-acting. Ephedrine, Amphetamine, Methyl-amphetamine and Methyl phenidate are several examples of noncatecholamines.
What are the Similarities Between Catecholamines and Noncatecholamines?
- Both catecholamines and noncatecholamines are neurotransmitters or hormones.
- They are adrenergic agonists which mimic the effects of adrenergic nerve stimulation.
- Metabolism and inactivation of both catecholamine and noncatecholamine occur in the liver.
What is the Difference Between Catecholamines and Noncatecholamines?
Catecholamines are direct-acting adrenergic drugs that have catechol. Noncatecholamines are adrenergic drugs that do not have catechol. So, this is the key difference between catecholamines and noncatecholamines. Moreover, catecholamines are direct-acting while noncatecholamines are direct-acting, indirect-acting, or dual-acting.
Moreover, another difference between catecholamines and noncatecholamines is that catecholamines cannot be used orally while noncatecholamines can be used orally. Furthermore, catecholamines have a short-half life while noncatecholamines have a longer-half life. Adrenaline, Nor-adrenaline, Isoprenaline, Dopamine, and Dobutamine are examples of catecholamines while Ephedrine, Amphetamine, Methyl-amphetamine, Methyl phenidate are examples of noncatecholamines.
The below infographic tabulates more differences between catecholamines and noncatecholamines for side by side comparison.
Summary – Catecholamines vs Noncatecholamines
Catecholamines and noncatecholamines are two types of adrenergic drugs. Catecholamines are direct-acting drugs while noncatecholamines are direct-acting, indirect-acting or dual-acting. Moreover, catecholamines have hydroxyl groups at position 3 and 4 on benzene ring while noncatecholamines lack one or both hydroxyl groups. Thus, this summarizes the difference between catecholamines and noncatecholamines.
Reference:
1. Paravati, Stephen. “Physiology, Catecholamines.” StatPearls [Internet]., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 26 July 2020, Available here.
2. “Catecholamine.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 17 Sept. 2020, Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Noradrenalin – Noradrenaline” By NEUROtiker – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vwK2cnKCfoa6utc2eqmaZnpl6r7vNnJitnZOdvK2tzKKlnqtfWIe%2FhtOer611c5bBpq%2FHqKOapZmjsrRxkWmtrF1iZZuwusKaq56bmKS5ornIp5ysZVx4rrWxwqGmpZmdnrumv4RrZ5qmlFp%2FcbrOp5qarJWYtbC4wKagp52jWn9xrdGeXGtopKy8Zn6PrbCpnaNaf3G7xV5paZmUp7KvsdGgoJxdYmWxs8HGrGVlXWJ5rqTAyKeeXmpgpL9mfo%2BdrJqkVWeRoq%2FToqWgZg%3D%3D