The key difference between carbon dots and quantum dots is that carbon dots are small carbon nanoparticles, whereas quantum dots are small semiconductor particles.
Both carbon dots and quantum dots fall under the field of quantum mechanics. These are small nanoscale particles.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What are Carbon Dots
3. What are Quantum Dots
4. Carbon Dots vs Quantum Dots in Tabular Form
5. Summary – Carbon Dots vs Quantum Dots
What are Carbon Dots?
Carbon dots are small carbon nanoparticle having some form of surface passivation. Their size is less than 10 nm. These dots were first discovered in 2004 accidentally through the purification of single-walled carbon nanotubes.
The properties of carbon dots solely depend on their structures and compositions. Most of the times, many carboxyl moieties on the carbon dots’ surface impart an excellent solubility in water and biocompatibility. These moieties tend to allow the carbon dots to serve as proton-conducting nanoparticles. Moreover, these particles are suitable for chemical modification and surface passivation alongside various organic, polymeric, inorganic or biological materials.
There are two methods of synthesis of carbon dots. Those two are the “top-down” method and the “bottom-up” method. We can achieve the production of the carbon dots through these processes via chemical, electrochemical and physical techniques.
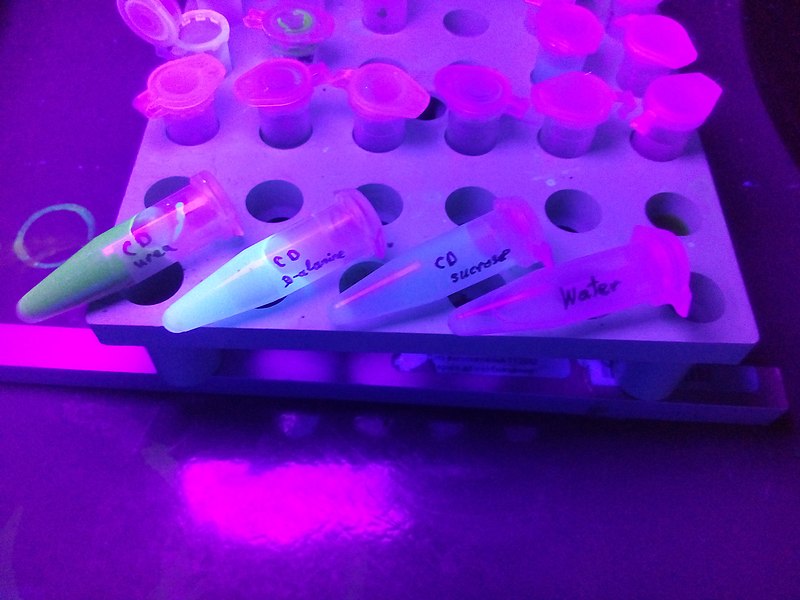
Figure 01: Carbon Dots Prepared from Different Sources
The “top-down” method involves the breaking down of large carbon structures (e.g. graphite, carbon nanotubes, and nanodiamond) into carbon dots with the use of laser ablation, arc discharge, and electrochemical method.
The “bottom-up” method of carbon dot production involves small precursors such as carbohydrates, citrate, and polymer silica nanocomposites. These sources undergo hydrothermal/solvothermal treatment, supported synthetic, and microwave synthetic routes.
What are Quantum Dots?
Quantum dots are small semiconductor particles on the nanometer scale, having optical and electronic properties that differ from large particles according to quantum mechanics. If we observe quantum dots through illumination under UV light, an electron in the quantum dot tends to get excited into a state having higher energy. This process corresponds to the transition of an electron from the valance band to the conductance band when concerning the semiconducting quantum dot. Then the excited electron can drop back into the valence band through the release of its energy via the emission of light. This light emission is named photoluminescence, and we can illustrate it as follows:

Figure 02: Photoluminescence of Quantum Dots Giving Different Colours from Quantum Dots with Different Sizes
Usually, the properties of quantum dots are intermediate to those of bulk semiconductors and discrete atoms or molecules. Moreover, the optoelectronic properties of quantum dots change as a function of both size and shape. Typically, large quantum dots emit long wavelengths, and the emitted colours from these quantum dots range from orange to red. In contrast, small quantum dots tend to emit shorter wavelengths giving rise to colours such as blue and green. However, we can observe that the colour can vary depending on the exact composition of the quantum dot.
The major applications of quantum dots include single-electron transistor manufacturing, solar cell production, LEDs production, single-photon sources, quantum computing, cell biology research, microscopy, and medical imaging.
What is the Difference Between Carbon Dots and Quantum Dots?
The key difference between carbon dots and quantum dots is that carbon dots are small carbon nanoparticles, whereas quantum dots are small semiconductor particles. Carbon dots are used in bioimaging, sensing, drug delivery, catalysis, optronics, etc., while quantum dots are used in single-electron transistor manufacturing, solar cell production, LEDs production, single-photon sources, quantum computing, cell biology research, microscopy, and medical imaging.
The following infographic lists the differences between carbon dots and quantum dots in tabular form.
Summary – Carbon Dots vs Quantum Dots
Carbon dots and quantum dots come under the field of quantum mechanics. These are small nanoscale particles. The key difference between carbon dots and quantum dots is that carbon dots are small carbon nanoparticles, whereas quantum dots are small semiconductor particles.
Reference:
1.“Carbon Quantum Dot.” An Overview | ScienceDirect Topics.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Carbon dots prepared by Paliienko K. Kiev Ukraine” By Nozhnici – Own work (CC BY-SA 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “QD S” By Walkman16 – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26vwKuZqKZdmby1v4yapZ1loaqur8DUpmSdp6SofA%3D%3D