Key Difference – Bronchitis vs Whooping Cough
The key difference between Bronchitis and Whooping Cough is that Bronchitis is the inflammation of the large and medium-sized airways (bronchi) of the lungs, usually caused by respiratory viruses and rarely by bacteria where as whooping Cough (pertussis) is a respiratory disease caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. It is a highly contagious and can be prevented by vaccination. Bronchitis can be a part of the disease manifestations of whooping cough.
What is Bronchitis?
Bronchitis is the inflammation of the large and medium-sized airways (bronchi) of the lungs, usually caused by respiratory viruses. It can be a part of the disease manifestations of whooping cough (pertussis).
Due to the inflammation caused in the bronchial mucosa it causes the symptoms of productive cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Bronchitis is divided into two types based on the duration.
Acute Bronchitis
Symptoms usually last around three weeks. In more than 90% of cases, it is caused by a viral infection. These viruses usually spread through the air when people cough or through direct contact commonly via hands. Therefore, hand washing is an important preventive measure. Risk factors include exposure to tobacco smoking, dust, and other air pollutants. Treatment of acute bronchitis involves rest, paracetamol, antihistamines and NSAIDs to help with symptoms.
Chronic Bronchitis
It is defined as a productive cough lasting over for three months or more per year for at least two years. Most people with chronic bronchitis have chronic obstructive airway disease (COPD) which is most commonly caused by tobacco smoking, with a number of other factors like air pollution and genetics playing a smaller role. Treatment of chronic bronchitis includes quitting smoking, vaccinations, pulmonary rehabilitation, supplemented with inhaled bronchodilators and steroids. Some people may benefit from long-term home oxygen therapy or lung transplantation during the later stages of the disease.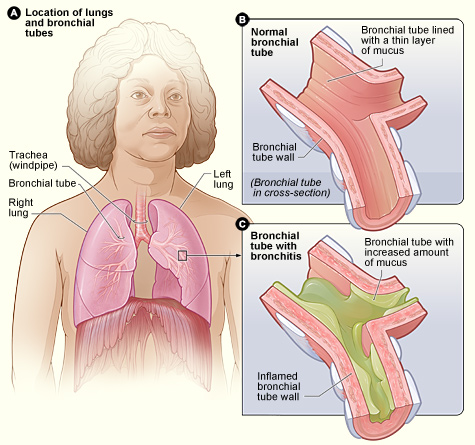
What is Whooping Cough?
Pertussis or whooping cough is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. It is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the nasal secretions of an infected person. It has the classic symptoms of a paroxysmal cough, inspiratory whoop and dizziness or vomiting after coughing. Other than the classic symptoms, it can lead to subconjunctival hemorrhages, rib fractures, urinary incontinence due to violent coughing. It has a long incubation period, which is typically seven to ten days with a range of four to 21 days and rarely even longer than that. In a complete blood count, Lymphocytosis is a diagnostic clue for whooping cough (pertussis), although it is not specific. Methods used in laboratory diagnosis include culturing of nasopharyngeal swabs, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and serological methods (antibody detection). The antibiotic of choice is erythromycin or azithromycin as the treatment. It is a vaccine preventable disease, and pertussis vaccine is recommended for routine use by the World Health Organization.
Pertussis vaccine is recommended for routine use by the World Health Organization.
What is the difference between Bronchitis and Whooping Cough?
Definition of Bronchitis and Whooping Cough
Bronchitis: Bronchitis is an inflammation of the air passages between the nose and the lungs, including the windpipe or trachea and the larger air tubes of the lung that bring air in from the trachea (bronchi).
Whooping cough: Whooping cough is an infectious disease caused by Bordetella pertussis, marked by catarrh of the respiratory tract and peculiar paroxysms of cough, ending in a prolonged crowing or whooping respiration.
Cause of Bronchitis and Whooping Cough
Bronchitis: Bronchitis is commonly caused by viruses.
Whooping cough: Whooping cough is almost always caused by Bordetella pertussis.
Characteristics of Bronchitis and Whooping Cough
Incubation period
Bronchitis: Bronchitis has a shorter incubation period.
Whooping cough: Whooping cough has a longer incubation period.
Symptoms
Bronchitis: In bronchitis, productive cough is typical.
Whooping cough: Paroxysmal cough, inspiratory whoop and dizziness are typical in whooping cough.
Treatment
Bronchitis: Medicines are given to control the symptoms of bronchitis.
Whooping cough: Whooping cough or Pertussis needs to be treated with Macrolides.
Prevention
Bronchitis: Bronchitis is not vaccine preventable.
Whooping cough: Whooping cough is vaccine preventable. Pertussis vaccine is recommended for routine use by the World Health Organization.
Reference Bronchitis. (n.d.) Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine. (2008). Retrieved August 13 2015 from http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/bronchitis Pertussis. (n.d.) Dorland’s Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers. (2007). Retrieved August 13 2015 from http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/pertussis Image Courtesy: “Bronchitis” by National Heart Lung and Blood Institute – National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. (Public Domain) via Wikimedia CommonsncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26u0ailnKCZqba0ecCnm2auo2LEqbvOqaCnn12YvLazx2g%3D