The key difference between biotin and keratin is that biotin is a water-soluble vitamin while keratin is a structural protein.
Biotin and keratin are essential components of the body that carry out many important functions. Unlike biotin, keratin is extremely water insoluble. Biotin takes part in metabolic activities while keratin functions as a protective protein.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Biotin
3. What is Keratin
4. Similarities Between Biotin and Keratin
5. Side by Side Comparison – Biotin vs Keratin in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Biotin?
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin. It is also referred to as vitamin B7. Biotin functions in a wide range of metabolic processes including the utilization of carbohydrates, fats and amino acids. Therefore, not only for humans, biotin is an important vitamin for other organisms too. Also, biotin actively participates as an enzyme component during the fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
Furthermore, biotin actively influences the cell growth and amino acids that involve in protein synthesis. Apart from this, biotin functions in metabolic reactions that involve transferring of carbon dioxide and help in maintaining constant blood sugar level.
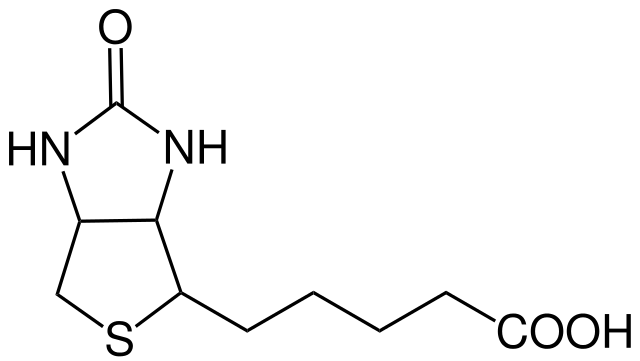
Figure 01: Biotin
In the context of cosmetics, biotin is recommended as a dietary supplement for hair and skin. However, our body needs biotin in smaller amounts. Consequently, biotin deficiency is extremely rare. Moreover, the biotin requirement for the body is mainly fulfilled by a wide range of food and intestinal microflora that synthesize biotin.
What is Keratin?
Keratin is a protein that belongs to the family of fibrous structural proteins. Hence, it could be defined as a protective protein. It is an organic solvent which is insoluble in water. Keratin is the key structural protein that makes up hair, nails and an outer layer of skin in humans and horns, claws and hooves in animals. It is also present in internal organs and glands. Keratin also functions to protect epithelial cells from damage and stress.
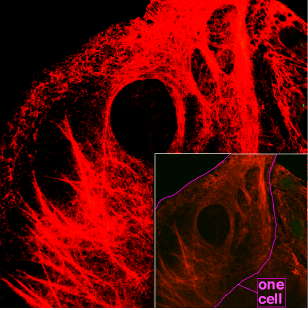
Figure 02: Keratin
Moreover, keratin monomers assemble in bundles to form intermediate filaments. These intermediate filaments are tough. Moreover, they are abundant in keratinocytes. Keratinocytes are proteins present in the cornified layer of the epidermis that has undergone keratinization. Hence, they form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages. These appendages are commonly present in reptiles, birds, amphibians and mammals.
What are the Similarities Between Biotin and Keratin?
- Both biotin and keratin act as supplements for hair and skin.
- Besides, biotin improves our body’s keratin infrastructure.
What is the Difference Between Biotin and Keratin?
Both biotin and keratin are extremely important components of our body. Biotin is a vitamin while keratin is a protein. Thus, this is a significant difference between biotin and keratin. To add to this, biotin is a water-soluble vitamin that belongs to vitamin family B7 while the keratin is a water-insoluble protein that belongs to a family of fibrous structural proteins. Therefore, we can consider this as the key difference between biotin and keratin.
Moreover, monomers of biotin are amides while the monomers of keratin are amino acids. Thus, it is also a difference between biotin and keratin.
Below infographic provides more details on the difference between biotin and keratin.
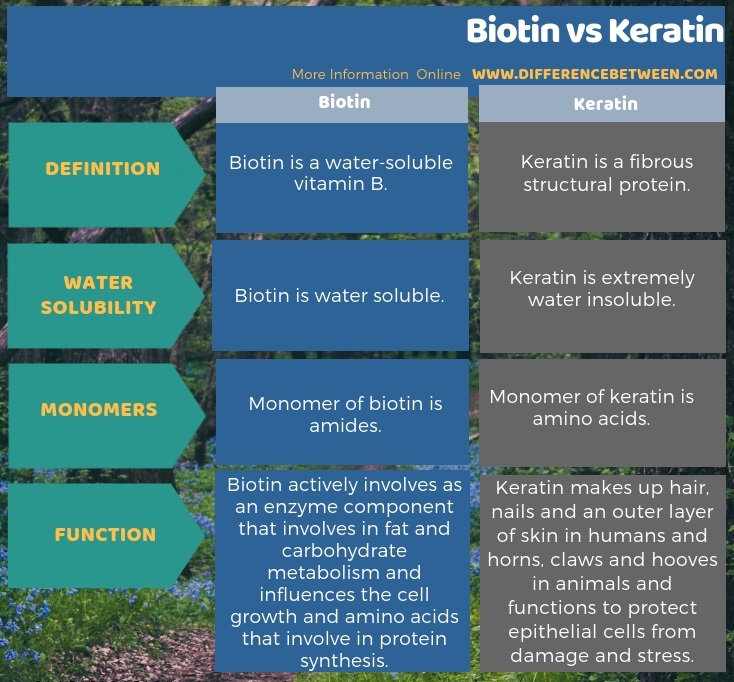
Summary – Biotin vs Keratin
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin in the family of vitamin B7. It actively involves an enzyme component that participates in fat and carbohydrate metabolism. Moreover, biotin is required in smaller amounts. Therefore, biotin deficiency is extremely rare. On the other hand, keratin is a fibrous structural protein. It is insoluble in water and organic solvents. Hence, the key difference between biotin and keratin is that the biotin is a water-soluble vitamin while keratin is water-insoluble structural protein. However, biotin improves the body’s keratin infrastructure. Thus, this is the summary of the difference between biotin and keratin.
Reference:
1. “Biotin: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Dosage, and Warning.” WebMD, WebMD. Available here
2. Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. “Keratin.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., 11 Jan. 2019. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.”Biotin”By Wesalius – Own work, (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2.”KeratinF9″ (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26uyKiroqZdlrulecqeqZqsmaN8