Key Difference – B Cell vs T Cell Lymphoma
Malignancies of the lymphoid system are known as lymphomas. They can arise at any place where lymphoid tissue is found. The incidence of several subtypes of the disease has increased over the years. The commonest presentation of the lymphomas is peripheral lymphadenopathy or symptoms due to occult lymph nodes. According to WHO classification, there are 2 types of lymphomas as Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Non- Hodgkin’s lymphoma is an umbrella term covering a multiple sub classified spectrum of B-and T-cell malignancies. Approximately 80% of NHL are of B-cell origin and the remaining 20% is of T-cell origin. This can be considered as the key difference between B cell and T cell lymphoma. The sub classification of NHL is done according to the cell of origin (T cell or B cell) and the stage of lymphocyte maturation at which the malignancy occurs (precursor and mature).
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is B Cell Lymphoma
3. What is T Cell Lymphoma
4. Similarities Between B Cell and T Cell Lymphoma
5. Side by Side Comparison – B Cell vs T Cell Lymphoma in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is B Cell Lymphoma?
Lymphoid system malignancies which are of B lymphocyte origin are known as B-cell lymphomas. About 80% of all NHL are of B cell origin. The principal subtypes of B cell lymphomas are Follicular lymphomas, Diffuse large B cell lymphomas, Burkitt’s lymphoma, Mantle cell lymphoma, and lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
Follicular Lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma is the second commonest NHL worldwide. These are rarely seen in children and usually occurs in middle aged or elderly people. Most of the patients experience painless lymphadenopathy at multiple sites. Some patients may present with B symptoms. In certain subtypes, bone marrow infiltration is common. Although the proportion of patients who have been completely cured of this condition is small, the newly introduced therapy (rituximab), which targets the CD20 antigen expressed on almost all B-cell lymphomas, seems to be very effective in combating the disease progression.
In up to 25% of the patients, transformation into diffuse large B-cell lymphoma can occur.
Management
Stage 1 – megavoltage irradiation
Stage 2 – Chemo immunotherapy incorporating Rituximab, CHOP-R (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone plus rituximab) and R-CVP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone)
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
It is the second commonest lymphoma in the childhood and the most common adult lymphoma worldwide. There is an overlap between classical diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt’s lymphoma. Occurrence in males is higher than in females.
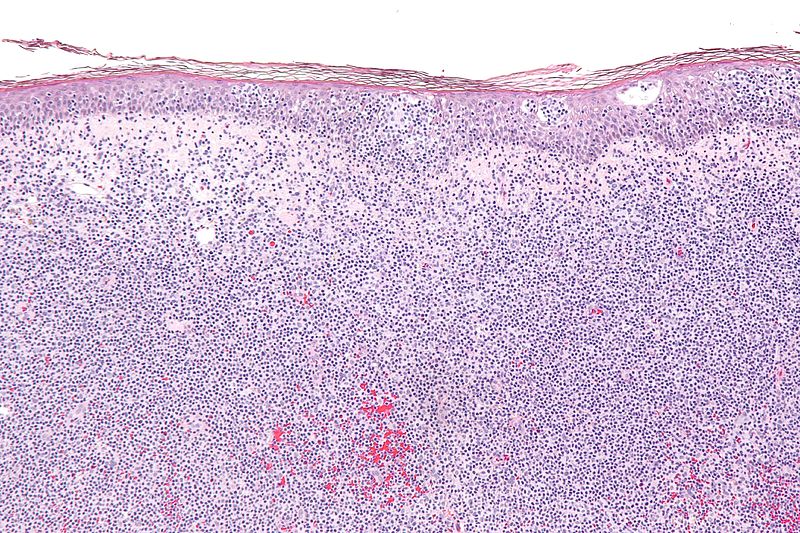
Figure 01: Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma
Clinical Features
- Painless lymphadenopathy
- Bowel symptoms
- ‘B’symptoms
Management
In a younger patient without risk factors, there is a huge possibility of a complete cure. Treatments should be initiated soon after the diagnosis.
Low-risk disease – ‘CHOP-R’ followed by involved field irradiation
Intermediate and poor risk – Chemoimmunotherapy, ‘CHOP-R’
Burkitt’s Lymphoma
The most rapidly proliferating lymphoma is Burkitt’s lymphoma, which possesses a very rapid doubling time. It is the commonest childhood malignancy worldwide. Incidence among females is higher than that among males. There are 3 main types of Burkitt’s lymphomas as Endemic (always Epstein-Barr virus-associated), Sporadic, AIDS- related. In the Western world, over the past 10 years, the prognosis of Burkitt’s lymphoma has markedly improved.
Clinical Features
- Jaw tumor
- Abdominal mass
Management
After the appropriate investigations, the patient should be made hemodynamically and metabolically stable prior to any therapy. Measures should be taken to minimize the tumor lysis syndrome. After treatment is commenced, monitoring of electrolytes should be done frequently. Standard treatment comprises a cyclic combination of chemotherapy.
What is T Cell Lymphoma?
Lymphomas which have a T lymphocyte origin are known as T-cell lymphomas. They account for 20% of all NHL. T-cell lymphomas are relatively common in the East. The commonest presentation of the disease is nodal and cutaneous, but in some of the specific subtypes, there can be liver and cutaneous tissue involvement. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas with the nodal presentation have a poor prognosis.
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma are the commonest subtypes of T cell lymphomas. The primary presentation of both forms is lymphadenopathy. ‘B’ symptoms are common in the T-cell lymphomas, unlike in B cell lymphomas. In angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphomas, features of an inflammatory disease, with fever, rashes and electrolyte abnormalities can be observed. These symptoms rapidly improve with the administration of corticosteroids or low dose of alkylating agents.
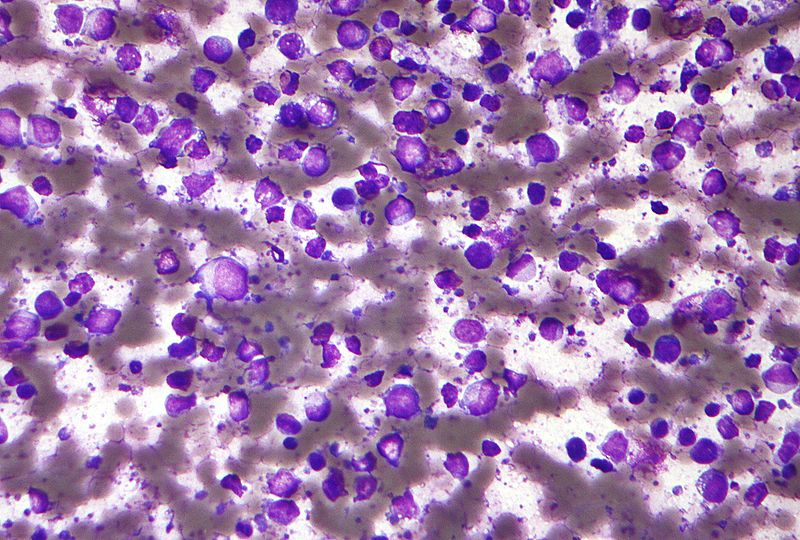
Figure 02: Cutaneous T Cell Lymphoma
Management
After the standard investigations, patients are treated with cyclical combination chemotherapy. As T- cells do not express CD20, Rituximab is not used in treating T-cell lymphomas. There is no equivalent drug for T-cell lymphomas. Along with treatment, resolution of the disease may occur but recurrences usually take place between the cycles. Second line therapy is not very satisfactory although myeloablative therapy may benefit a small proportion of patients.
What are the Similarities Between B Cell and T Cell Lymphoma?
- Both types of lymphomas arise from the lymphoid tissues
What is the Difference Between B Cell and T Cell Lymphoma?
B Cell vs T Cell Lymphoma | |
| Lymphoid system malignancies which are of B lymphocyte origin are known as B-cell lymphomas. | Lymphomas which have a T lymphocyte origin are known as T-cell lymphomas. |
| Prognosis | |
| Prognosis is relatively good. | In comparison to B cell lymphomas, T cell lymphomas have a poor prognosis. |
| Treatment | |
| Rituximab is used in the treatment. | Rituximab cannot be used in the treatment. |
Summary – B Cell vs T Cell Lymphoma
The difference between B cell and T cell lymphoma lies mainly in their origin; lymphoid malignancies which are of B lymphocyte origin are known as B-cell lymphomas while lymphomas which have a T lymphocyte origin are known as T-cell lymphomas. Diagnosis of these malignancies in their preliminary stages drastically improves the disease prognosis. Therefore, medical advice should be taken if a person has any of the warning signs that have been discussed in this article.
Download PDF Version of B Cell vs T Cell Lymphoma
You can download PDF version of this article and use it for offline purposes as per citation note. Please download PDF version here Difference Between B Cell and T Cell Lymphoma.
References:
1. Kumar, Parveen J., and Michael L. Clark. Kumar & Clark clinical medicine. Edinburgh: W.B. Saunders, 2009. Print.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Diffuse large B cell lymphoma – cytology low mag” By Nephron – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma – intermed mag” By Nephron – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26ujJycpaRdlruledWsZK1lk5q5rXnLsqSpoJ%2BirnA%3D