The key difference between autoecious rust and heteroecious rust is that autoecious rust is a parasitic fungus which can complete its life cycle on a single host species, while heteroecious rust is a parasitic fungus that requires two or more host species to complete its life cycle.
Rust is a plant disease caused by parasitic fungi. Therefore, these fungi are common as rust fungi. They are complex plant pathogens. Since they are parasites, they cannot exist as saprophytes. Thus, they need a host organism to survive, derive nutrients and complete the life cycle. Furthermore, many rust fungi need two or more host species to complete their life cycle. Based on the number of host species they require, there are two rust fungi as autoecious rust and heteroecious rust. Autoecious rust uses only one host species while heteroecious rust uses two or more host species to complete its life cycle.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Autoecious Rust
3. What is Heteroecious Rust
4. Similarities Between Autoecious Rust and Heteroecious Rust
5. Side by Side Comparison – Autoecious Rust vs Heteroecious Rust in Tabular Form
6. Summary
What is Autoecious Rust?
Autoecious rust is an obligate parasitic fungus that needs a single host species to complete its life cycle. So, autoecious rust fungus spends all stages of the life cycle in one specific host organism.
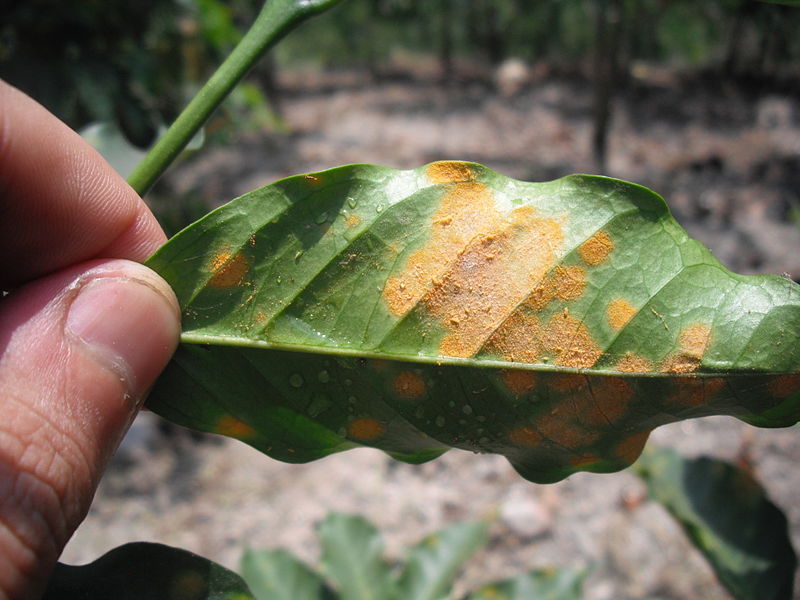

Figure 01: Autoecious Rust – Coffee Leaf Rust
Fungi belonging to Urediniomycetes are autoecious rust fungi. Autoecious rusts commonly attack asparagus, bean, chrysanthemum, coffee, hollyhock, snapdragon, and sugarcane.
What is Heteroecious Rust?
Heteroecious rust is an obligate parasitic fungus that needs at least two hosts or more hosts to complete its life cycle. The identification of alternate hosts of heteroecious rust is extremely difficult. It is because they produce different types of spores, and the spore morphology is complex.
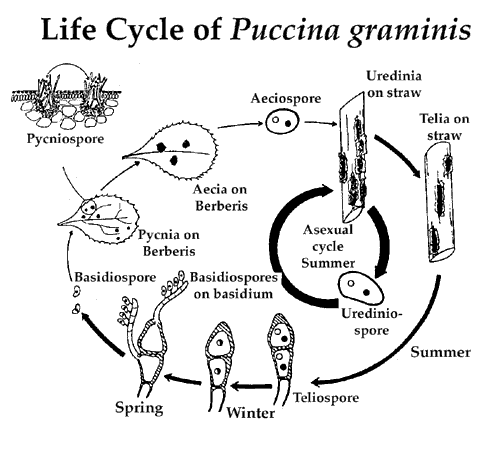
Figure 02: Heteroecious Rust – Puccina graminis
Gymnosporangium, Cronartium ribicola, Puccinia graminis, Puccinia coronata, Phakopsora meibomiae and P. pachyrhizi are several heteroecious fungal species.
What are the Similarities Between Autoecious Rust and Heteroecious Rust?
- Autoecious rust and heteroecious rust are two types of obligate parasitic fungi.
- They are plant pathogens that cause rust diseases in plants.
- Both types of fungi need host species to complete their life cycle.
- Thus, they are completely dependent on the presence of living plant hosts to reproduce and complete their life cycles.
- Moreover, they show a high degree of host specificity as well.
What is the Difference Between Autoecious Rust and Heteroecious Rust?
Autoecious rust is a parasitic fungus that colonizes single host while heteroecious rust is a fungus that colonizes two or more hosts. So, this is the key difference between autoecious rust and heteroecious rust. Furthermore, autoecious rust forms two types of spores, while heteroecious rust forms five types of spores.
The below infographic shows more comparisons regarding the difference between autoecious rust and heteroecious rust.
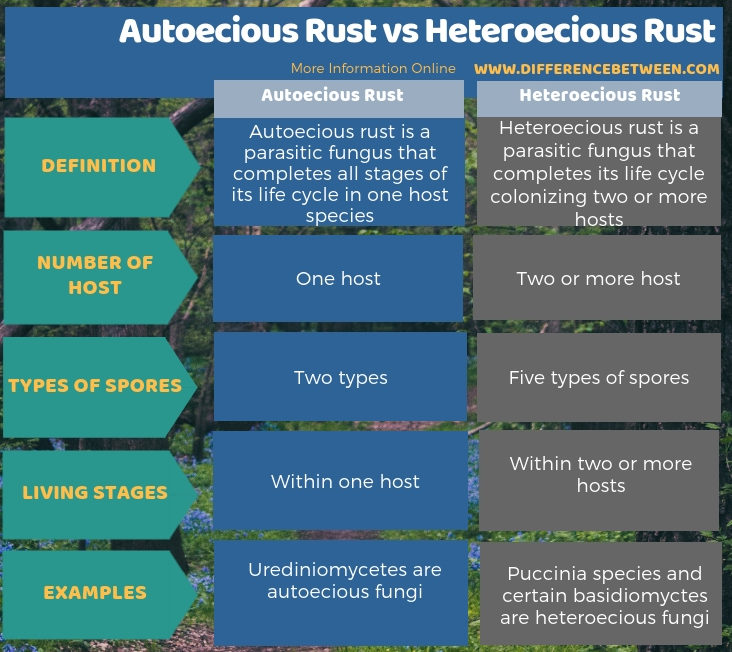
Summary – Autoecious Rust vs Heteroecious Rust
In summary, rust is a plant disease caused by obligate parasitic fungi. Moreover, based on the number of host species needed to complete their life cycle, rusts have two types as autoecious rust and heteroecious rust. Here, the autoecious rust colonizes one host species to complete the life cycle while heteroecious rust colonizes two or more host species to complete the life cycle. Therefore, this is the key difference between autoecious rust and heteroecious rust.
Reference:
1. “Heteroecious.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 3 Aug. 2018, Available here.
2. “Rust.” Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., Available here.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Hemileia vastatrix – coffee leaf rust” By Smartse – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Puccina graminis lifecycle” (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26t1K2mnpuZpMK0edGuqq1lkaOxbrTErZyrp5WYtrDB0maprqukZA%3D%3D