The key difference between atomic oxygen and molecular oxygen is that the atomic oxygen is highly reactive and does not exist in the atmosphere as it is whereas the molecular oxygen is less reactive and exists in the atmosphere as it is. Moreover, atomic oxygen is a free radical having the symbol O(3P) while the molecular oxygen is a diatomic oxygen having the symbol O2.
Oxygen is a chemical element having the atomic number 8. But when we refer to oxygen in common use, we are talking about molecular oxygen that we breathe. It has two oxygen atoms bonded to each other via covalent bond. Atomic oxygen has one oxygen atom. Therefore, it cannot exist as an individual chemical species because of its high reactivity.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Atomic Oxygen
3. What is Molecular Oxygen
4. Side by Side Comparison – Atomic Oxygen vs Molecular Oxygen in Tabular Form
5. Summary
What is Atomic Oxygen?
Atomic oxygen is a very reactive chemical species having the symbol O(3P). It is a free radical. This means atomic oxygen has an unpaired electron that makes this atom highly reactive. Therefore, this atom does not exist naturally for even a short period; it tends to react with other chemical elements or compounds to become stable by pairing its unpaired electron.
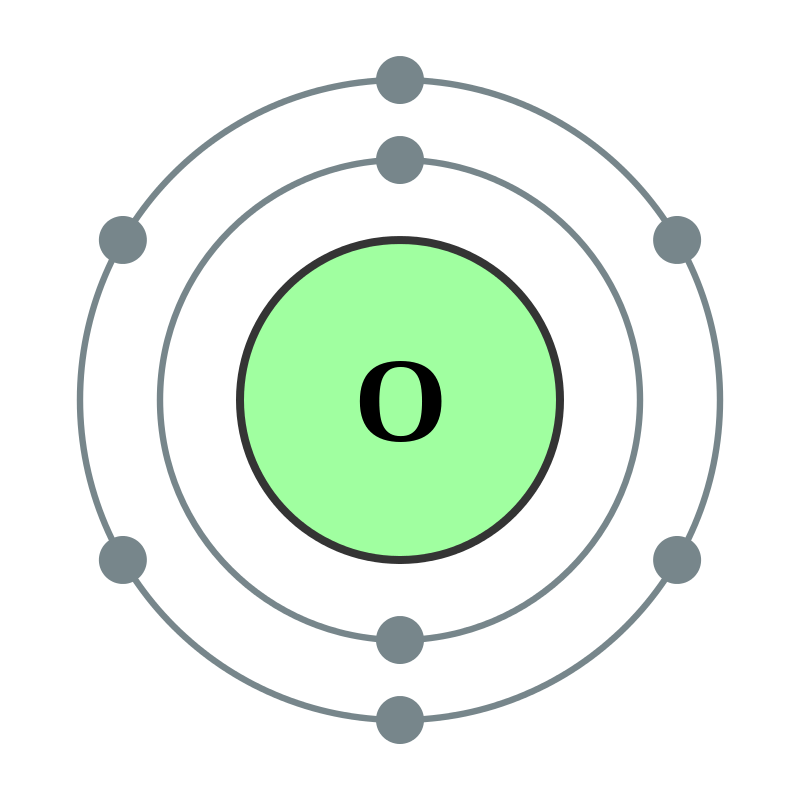
Figure 01: Oxygen Atom
However, in outer space, about 96% of oxygen exists as atomic oxygen because there UV radiation results in a low earth orbits atmosphere. This chemical species plays a major role in corrosion in space. Corrosion in space is the corrosion of materials occurring in outer space.
What is Molecular Oxygen?
Molecular oxygen is diatomic oxygen having the symbol O2. It contains two oxygen atoms bonded to each other via covalent bonding. There is a double bond between these two atoms. Since the two oxygen atoms have eight electrons around them, the oxygen molecule is less reactive.
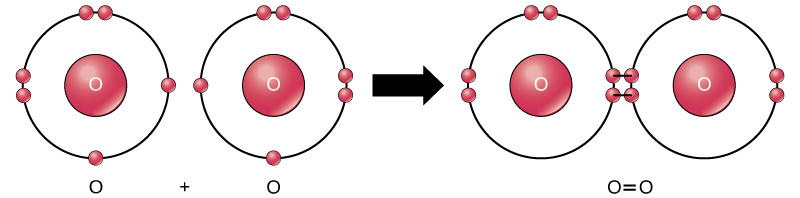
Figure 02: Formation of Molecular Oxygen
Therefore, this chemical species exist in the atmosphere itself. Our atmosphere has about 21% molecular oxygen. This amount of oxygen is essential for all the organisms for their respiration. It exists as a colorless gas and the boiling point is −183 °C.
What is the Difference Between Atomic Oxygen and Molecular Oxygen?
Atomic oxygen is a very reactive chemical species having the symbol O(3P). It does not exist naturally for even a short period, but in outer space, it is the predominant form of oxygen. Moreover, it is highly reactive. Molecular oxygen is diatomic oxygen which has the symbol O2. It exists as itself in our atmosphere (about 21%). In addition, it is less reactive.
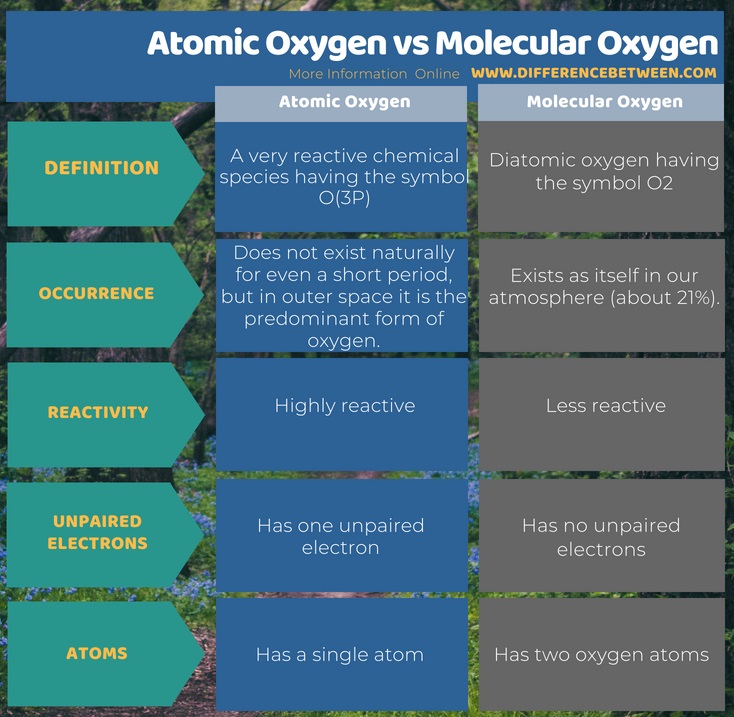
Summary – Atomic Oxygen vs Molecular Oxygen
Atomic and molecular oxygen are chemical species derived from the chemical element, oxygen which has the atomic number 8. The difference between atomic oxygen and molecular oxygen is that atomic oxygen is highly reactive and does not exist in the atmosphere as it is whereas molecular oxygen is less reactive and exists in the atmosphere as it is.
Reference:
1. “Allotropes of Oxygen.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 26 May 2018. Available here
2. Leenhouts, Doug. “The Differences of Oxygen & Oxygen Gas.” Sciencing, 24 Apr. 2017. Available here
Image Courtesy:
1.’Electron shell 008 Oxygen – no label’By Pumbaa (original work by Greg Robson) (CC BY-SA 2.0 uk) via Commons Wikimedia
2.’Figure 02 01 09’By CNX OpenStax, (CC BY 4.0) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26t06ikoptdpMW6s8SnZJqmlGK6sLjEnKylmaJivLnFxp6laA%3D%3D