Key Difference – Alkyl vs Aryl Group
Functional groups are a part of organic molecules that have the characteristic properties of a certain molecule. Some examples of these functional groups include alcohols, carboxylic acid groups, amine groups, etc. These functional groups are side groups of the main carbon chain. In other words, functional groups are a part of a large molecule. It can be an atom, a group of atoms or even an ion. Most of the times these groups are responsible for the reactions that the molecule may undergo. These functional groups should be taken into account when naming any organic molecule. A functional group always have a vacant position in its structure for it to get attached to a carbon chain. The main difference between alkyl and aryl is that alkyl group has no aromatic ring whereas aryl group has an aromatic ring.
CONTENTS
1. Overview and Key Difference
2. What is Alkyl Group
3. What is Aryl Group
4. Side by Side Comparison – Alkyl vs Aryl Group
5. Summary
What is an Alkyl Group?
An alkyl group is a functional group that can be found in organic molecules. It is an alkane with hydrogen atom missing from its chain. This vacant point can be attached to a carbon atom of a carbon chain. This alkyl group can be a simple, branched or cyclic chain, but it does not have aromatic rings. Alkyl groups have only carbon and hydrogen atoms in their structure. The general formula of an alkyl group can be given as CnH2n+1 which is different from the formula of an alkane, CnH2n+2 with the loss of a hydrogen atom. Thus, alkyl groups are derived from alkanes. The smallest alkyl group is methyl group which can be given as –CH3. It has been derived from the alkane methane (CH4). Sometimes one tends to confuse cycloalkyl groups with aromatic groups. But there is a huge difference between them. Cycloalkanes are saturated and have no double bonds, but aromatic rings are unsaturated and have double bonds in their structure (for example Cyclohexane). The word saturated implies, it has the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that it can bond with. Even in morphology, cycloalkanes are 3D structures whereas aromatic compounds are planar structures. Hence, all alkyl groups are saturated because alkyl groups are derived from alkanes. The following examples show different propyl groups.

Figure 01: Propyl groups
What is an Aryl Group?
An aryl group always contains an aromatic ring. Aryl group is a simple aromatic compound with one of its hydrogen atoms missing. This missing hydrogen atom allows it to get attached to a carbon chain. The most common aromatic ring is benzene. All aryl groups are derived from benzene structures. Some examples of aryl groups include phenyl group derived from benzene and naphthyl group derived from naphthalene. These aryl groups can have substitutions in their aromatic structure. For example, tolyl group is derived from toluene where toluene is a benzene ring with the substitution of a methyl group. All aryl groups are unsaturated. That means the structure of aryl groups are composed of double bonds. But benzene is not the only type of aromatic ring that aryl groups can have. For example, indolyl group is an aryl group attached to the common amino acid, tryptophan. The following image shows the phenyl group which is derived from a benzene ring.
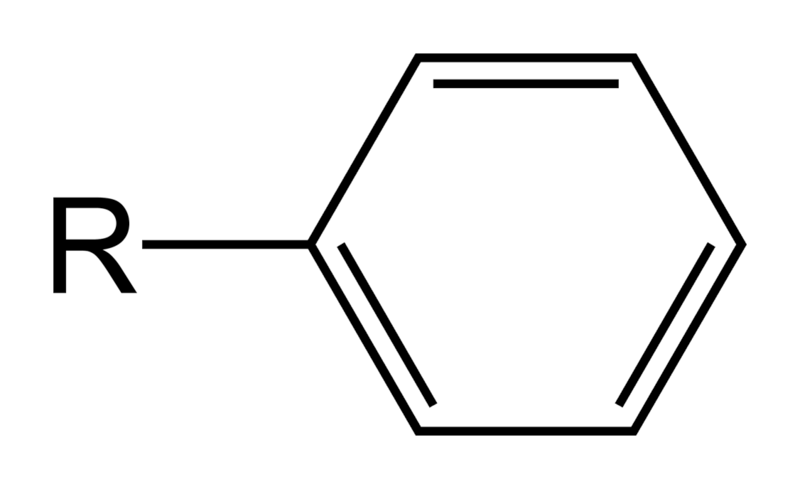
Figure 02: Phenyl group
What is the difference between Alkyl and Aryl Groups?
Alkyl vs Aryl Groups | |
| Alkyl groups are functional groups derived from alkanes. | Aryl groups are functional groups derived from aromatic rings. |
| Aromatic Ring | |
| Alkyl groups have no aromatic rings | Aryl groups are made of aromatic rings |
| Morphology | |
| Alkyl groups can be linear, branched or cyclic structures. | Aryl groups are essentially cyclic structures. |
| Saturation | |
| Alkyl groups are always saturated. | Aryl groups are unsaturated. |
| Stability | |
| Compounds having alkyl groups are less stable than those having aryl groups. | Compounds having aryl groups are more stable due to the presence of the aromatic ring. |
Summary – Alkyl vs Aryl Groups
Organic compounds can be linear, branched or cyclic and may have functional groups attached to it. Alkyl groups and aryl groups are two examples of functional groups. Both alkyl and aryl groups have carbon and hydrogen atoms. The main difference between alkyl and aryl groups is that alkyl groups do not have aromatic rings whereas aryl groups have aromatic rings in their structure.
Reference:
1. Helmenstine, A. M., 2016. ThoughtCo.. [Online] Available at: https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-aryl-group-604794[Accessed 29 05 2017].
2. Diana, n.d. Emaze. [Online] Available at: https://www.emaze.com/@ATLOCLTT/HYDROCARBONS[Accessed 29 05 2017].
Image Courtesy:
1. “Phenyl-group” (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
2. “Propyl groups” By Shoyrudude555 – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
ncG1vNJzZmivp6x7pbXFn5yrnZ6YsqOx07CcnqZemLyue8OinZ%2Bdopq7pLGMm5ytr5Wau26ty6SwpWWRo7FuwtJmmKuxnGK0s7vUqWY%3D